A drug-drug co-amorphous system for highly improved solubility of breviscapine: an experimental and computational study
- PMID: 39732994
- PMCID: PMC11682056
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-82524-2
A drug-drug co-amorphous system for highly improved solubility of breviscapine: an experimental and computational study
Erratum in
-
Author Correction: A drug-drug co-amorphous system for highly improved solubility of breviscapine: an experimental and computational study.Sci Rep. 2025 Apr 23;15(1):14171. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-98164-z. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40269107 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Correction: A drug-drug co-amorphous system for highly improved solubility of breviscapine: an experimental and computational study.Sci Rep. 2026 Jan 20;16(1):2540. doi: 10.1038/s41598-026-36294-8. Sci Rep. 2026. PMID: 41559149 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
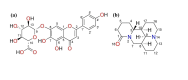
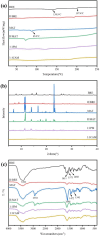
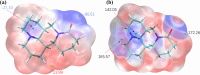
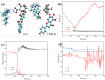
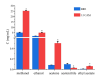
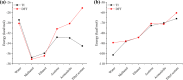
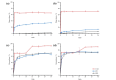
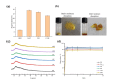
Drug-drug co-amorphous systems are a promising approach to improve the aqueous solubility of poorly water-soluble drugs. This study explores the combination of breviscapine (BRE) and matrine (MAT) form an amorphous salt, aiming to synergistically enhance the solubility and dissolution of BRE. In silico analysis of electrostatic potential and local ionization energy were conducted on BRE-MAT complex to predict the intermolecular interactions, and solvent-free energies were calculated using thermodynamic integration and density functional theory. The co-amorphous mixture, prepared by solvent evaporation, was characterized using various analytical techniques, including polarized microscopy, differential scanning calorimetry, and powder X-ray diffraction, confirming its amorphous nature. Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy and molecular dynamic simulations revealed strong hydrogen bonding, with a proton transfer from the carboxyl group of BRE to the tertiary amine nitrogen of MAT. The resulting co-amorphous salt demonstrated substantial solubility improvement (> 8000-fold in water) and enhanced in vitro dissolution of BRE. The study also confirmed that the co-amorphous salt maintained physical stability at 40 °C and 75% relative humidity over 6 months. These findings provide a viable strategy for developing drug-drug co-amorphous formulations to enhance solubility and stability, with significant potential for pharmaceutical applications.
Keywords: Brevascapine; Co-amorphous system; Intermolecular interaction; Matrine; Molecular dynamics simulation; Salt formation; Solubility enhancement.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 81960719/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 82360778/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 202001AZ070001-011/Applied Basic Research Joint Special Funds of Chinese Medicine
- 202205AC160038/The Reserve Talents Project for Young and Middle-Aged Academic and Technical Leaders of Yunnan Province
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

