Experimental study on optimization of pipe jacking mud mixture ratio based on MICP technology
- PMID: 39733016
- PMCID: PMC11682141
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-83133-9
Experimental study on optimization of pipe jacking mud mixture ratio based on MICP technology
Abstract
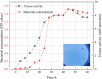
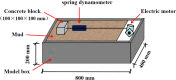
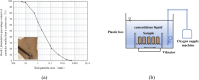
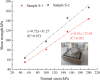
In the course of pipe jacking construction, the carrying-soil effect frequently arises, influenced by factors such as excavation unloading, ongoing disturbance from successive pipe sections, and the progressive accumulation of soil adhesion. The pipe jacking slurry serves as a critical agent for friction reduction and strata support, essential for the secure advancement of the construction process. This study introduces the Microbial-Induced Calcium Carbonate Precipitation (MICP) technology into the realm of pipe jacking slurry, aiming to enhance its friction-reduction capabilities and the stability of the soil enveloping the pipe. An optimal MICP-slurry formulation was determined using the uniform design approach. Subsequent model tests were carried out to assess the friction-reducing efficacy of the MICP-slurry, while the mechanism by which the MICP-slurry reinforces strata stability was investigated through soil mechanics and scanning electron microscopy (SEM) analyses. The findings indicate that the optimal MICP-slurry composition is as follows: bentonite: sodium carboxymethyl cellulose: soda ash: polyacrylamide: xanthan gum = 12%: 0.31%: 0.36%: 0.25%: 0.54%. The MICP-slurry achieves a 42.2% reduction in the friction coefficient between the test block and the sand. In comparison with the untreated sample, the cohesion of the MICP-treated sample is enhanced by 38.12%, and the internal friction angle increases by 14.01%. SEM examination reveals that the calcium carbonate crystals precipitated by the MICP-slurry within the soil populate the pores, increase the inter-particle bite force, and bolster the soil's mechanical characteristics.
Keywords: Carrying-soil effect; Friction reduction effect; MICP; Mechanical properties; Microstructure; Mud.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Zhang, R. X. et al. Shadowing effect of an existing tunnel on the evolution of soil arching: impact of tunnel shape. Can. Geotech. J., (2024).
-
- Shen Leilei. Impact of pipe jacking construction on surface and structure deformation and performance test of drag reduction slurry.2019.
-
- Ciaran, C. R. & Trevor, L. L. .Orr.Physical modelling of the effect of lubricants in pipejacking. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. incorporating Trenchless Technol. Res.63, 44–53 (2017). - DOI
-
- Yu Jun, Li, Y. Influence of physical properties of pipe jacking slurry sheath on jacking force. China Civil Eng. J.48 (S2), 327–331 (2015).
-
- J.Yen and K.Shou.Numerical simulation for the estimation the jacking force of pipe jacking.Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology incorporating Trenchless Technology Research,2015,49:218–229.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

