The effect of push frequency and stroke time on wheelchair maneuverability among wheelchair tennis athletes on hard tennis court
- PMID: 39733074
- PMCID: PMC11682048
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-83127-7
The effect of push frequency and stroke time on wheelchair maneuverability among wheelchair tennis athletes on hard tennis court
Abstract
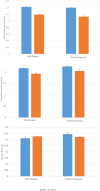
Wheelchair propulsion is a fundamental skill in wheelchair sports, particularly in wheelchair tennis. To achieve optimal mobility during wheelchair athletic performance, it is essential to consider propulsion techniques. This study examines the effect of push frequency and stroke duration on wheelchair maneuverability, measured by velocity during propulsion, among wheelchair tennis athletes. The athletes (N = 9; 5 elite and 4 novice) performed three tests; namely the comfortable speed propulsion test, sprint test and round-trip test; with and without holding their racquet, over their hard court. Results revealed that push frequency had positive correlation with propulsion velocity (r = 0.840, p < 0.001) while stroke time was negatively correlated with velocity (r = -0.859, p < 0.001). Propulsion performance between elite and novice wheelchair athletes, and between propelling with and without racquet were also reflected through these parameters. The rate of perceived exertion (RPE) had significantly positive but low correlation with velocity and push frequency, and significant negative correlation with stroke time. This study could serve as a recommendation for wheelchair tennis athletes and coaches in planning their training protocols and techniques.
Keywords: Propulsion; Push frequency; Stroke time; Wheelchair athletes; Wheelchair tennis.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing financial and non-financial interests.
Figures


References
-
- Van der Slikke, R., Berger, M., Bregman, D. & Veeger, D. Push Characteristics in Wheelchair Court Sport Sprinting. Proc. Eng.147, 730–734. 10.1016/j.proeng.2016.06.265 (2016). - DOI
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

