Monocytes to Apolipoprotein A1 ratio is associated with metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease in type 2 diabetes mellitus
- PMID: 39733102
- PMCID: PMC11682227
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-82994-4
Monocytes to Apolipoprotein A1 ratio is associated with metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease in type 2 diabetes mellitus
Erratum in
-
Author Correction: Monocytes to Apolipoprotein A1 ratio is associated with metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease in type 2 diabetes mellitus.Sci Rep. 2025 Mar 7;15(1):8032. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-90119-8. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40055381 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
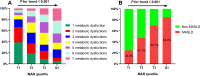
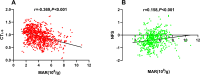
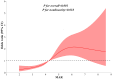
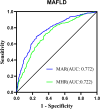
The monocyte-to-Apolipoprotein A1 ratio (MAR) emerges as a potentially valuable inflammatory biomarker indicative of metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease (MASLD). Accordingly, this investigation primarily aims to assess the correlation between MAR and MASLD risk. A cohort comprising 957 individuals diagnosed with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) participated in this study. The relationship between MAR and MASLD was analyzed through binomial logistic regression analysis and restricted cubic splines (RCS). Furthermore, a comparative assessment of MAR and monocyte to high-density lipoprotein ratio (MHR) in identifying MASLD efficacy was conducted using receiver operating characteristic curve analysis. Remarkably, even after adjusting for metabolic parameters and hepatic functional markers, MAR stood out as an independent predictor for MASLD (OR 1.58, 95% CI 1.36-1.84; P < 0.001) and displayed a nonlinear positive association with MASLD risk according to RCS analysis (P for nonlinearity and overall < 0.001). Notably, MAR exhibited superior diagnostic accuracy for identifying MASLD compared to MHR (AUC: 0.772 vs 0.722, P < 0.001). In summary, MAR emerges as a promising inflammatory indicator for MASLD, demonstrating potential as a valuable screening tool to bolster the management of MASLD within the T2DM population.
Keywords: Inflammatory marker; Metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease; Monocyte to Apolipoprotein A ratio; Type 2 diabetes mellitus.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors report no conflicts of financial and non-financial interests in this work.
Figures

References
-
- Gratchev, A., Sobenin, I., Orekhov, A. & Kzhyshkowska, J. Monocytes as a diagnostic marker of cardiovascular diseases. Immunobiology.217(5), 476–82 (2012). - PubMed
-
- Ferreiro-Iglesias, R., Barreiro-de Acosta, M., López-Díaz, J., Bastón Rey, I. & Domínguez-Muñoz, J. E. Usefulness of peripheral blood monocyte count to predict relapse in patients with inflammatory bowel disease: A prospective longitudinal cohort study. Rev. Esp. Enferm. Dig.114(1), 10–5 (2022). - PubMed
-
- Jack, et al. Association of peripheral total and differential leukocyte counts with metabolic syndrome and risk of ischemic cardiovascular diseases in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabet. Metabol. Res. Rev.23(2), 111–118 (2007). - PubMed
-
- Oeztuerk, et al. A nonclassical monocyte phenotype in peripheral blood is associated with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: a report from an EMIL subcohort. Hormone Metabol. Res.48, 54–61 (2016). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

