T cell induced expression of Coronin-1A facilitates blood-brain barrier transmigration of breast cancer cells
- PMID: 39733107
- PMCID: PMC11682172
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-83301-x
T cell induced expression of Coronin-1A facilitates blood-brain barrier transmigration of breast cancer cells
Abstract
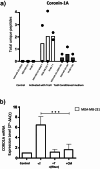
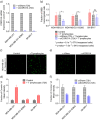
In previous work we discovered that T lymphocytes play a prominent role in the rise of brain metastases of ER-negative breast cancers. In the present study we explored how T lymphocytes promote breast cancer cell penetration through the blood brain barrier (BBB). An in vitro BBB model was employed to study the effects of T lymphocytes on BBB trespassing capacity of three different breast carcinoma cell lines. Differential protein expression was explored by comparing the proteomes of the breast cancer cells before and after co-culture with activated T lymphocytes using liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC-MS). siRNA was used to silence protein expression in the breast cancer cells to study contribution to in vitro BBB passage. Furthermore, protein expression in primary breast cancer tissues was explored and related to brain-metastatic potential. Co-culturing with activated T lymphocytes or their conditioned medium (CM) resulted in increased passage through the in vitro BBB. The effects were less for cell line MDA-MB-231-B2M2 (brain affinity) as compared to MDA-MB-231 and SK-BR-7. Mass spectrometry-based proteomics revealed significant alterations in the expression of 35 proteins by the breast cancer cell lines upon T cell contact. Among the proteins is coronin-1 A, a protein related to cell motility. Knockdown of CORO1A in the breast cancer cells reduced their ability to cross the artificial BBB to 60%. The effects were significantly less for the cell line derived from breast cancer with affinity for brain. The expression of coronin-1A was confirmed by immunohistochemistry and RT-PCR of 52 breast cancer samples of patients with metastasized breast cancers, with and without brain locations. Lastly, CORO1A upregulation was validated in a publicly available mRNA expression database from 204 primary breast cancers with known metastatic sites. We conclude that T lymphocytes trigger cancer cells to express proteins including coronin-1A that enable the cancer cells to cross an in vitro BBB. In addition, a prominent role of coronin-1A in the formation of cerebral metastases in breast cancer patients is strongly suggestive by its upregulation in tissue samples of breast cancer patients with brain metastases.
Keywords: Blood–brain barrier; Brain metastasis; Breast cancer; Coronin-1A; Liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry; Proteomics.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Consent for publication: All authors have seen and approved the text for publication. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests. Ethics approval and consent: Institutional Review Board Statement: This study was approved by the Medical Ethics Committee of the Erasmus Medical Center, Rotterdam, The Netherlands (MEC 02·953) and performed in adherence to the Code of Conduct of the Federation of Medical Scientific Societies in the Netherlands ( http://www.fmwv.nl/ ). Informed Consent Statement: Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Figures
Similar articles
-
T lymphocytes facilitate brain metastasis of breast cancer by inducing Guanylate-Binding Protein 1 expression.Acta Neuropathol. 2018 Apr;135(4):581-599. doi: 10.1007/s00401-018-1806-2. Epub 2018 Jan 19. Acta Neuropathol. 2018. PMID: 29350274 Free PMC article.
-
Cancer-associated fibroblast promote transmigration through endothelial brain cells in three-dimensional in vitro models.Int J Cancer. 2014 Nov 1;135(9):2024-33. doi: 10.1002/ijc.28848. Epub 2014 Mar 28. Int J Cancer. 2014. PMID: 24643985
-
Comparative membrane proteomics analyses of breast cancer cell lines to understand the molecular mechanism of breast cancer brain metastasis.Electrophoresis. 2017 Sep;38(17):2124-2134. doi: 10.1002/elps.201700027. Epub 2017 Jul 5. Electrophoresis. 2017. PMID: 28523741
-
Role of the blood-brain barrier in the formation of brain metastases.Int J Mol Sci. 2013 Jan 11;14(1):1383-411. doi: 10.3390/ijms14011383. Int J Mol Sci. 2013. PMID: 23344048 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Impact of breast cancer cells´ secretome on the brain metastatic niche remodeling.Semin Cancer Biol. 2020 Feb;60:294-301. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2019.10.011. Epub 2019 Nov 9. Semin Cancer Biol. 2020. PMID: 31711993 Review.
References
-
- Schouten, L. J. et al. Incidence of brain metastases in a cohort of patients with carcinoma of the breast, colon, kidney, and lung and melanoma. Cancer94 (10), 2698–2705 (2002). - PubMed
-
- Hatiboglu, M. A., Akdur, K. & Sawaya, R. Neurosurgical management of patients with brain metastasis. Neurosurg. Rev.43 (2), 483–495 (2020). - PubMed
-
- Lassman, A. B. & DeAngelis, L. M. Brain metastases. Neurol Clin. 21(1), 1–23, vii (2003). - PubMed
-
- Barnholtz-Sloan, J. S. et al. Incidence proportions of brain metastases in patients diagnosed (1973 to 2001) in the Metropolitan Detroit Cancer Surveillance System. J. Clin. Oncol.22 (14), 2865–2872 (2004). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

