Targeting Deltex E3 Ubiquitin Ligase 2 Inhibits Tumor-associated Neutrophils and Sensitizes Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells to Immunotherapy
- PMID: 39733452
- PMCID: PMC11831464
- DOI: 10.1002/advs.202408233
Targeting Deltex E3 Ubiquitin Ligase 2 Inhibits Tumor-associated Neutrophils and Sensitizes Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells to Immunotherapy
Abstract
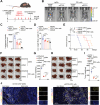
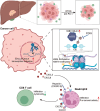
Several E3 ligases have been found to affect the immune microenvironment of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) and lead to the resistance of immunotherapy. In this study, genes of E3 ligases are screened based on The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) dataset. Through cytometry by time of flight (CyTOF), flow cytometry, and further experiments, Deltex E3 ubiquitin ligase 2 (DTX2) in HCC cells is identified to promote the infiltration and polarization of tumor-associated neutrophils (TANs) with a protumor phenotype, thus attenuating the infiltration and cytotoxicity of CD8+ T cells partially through C-X-C motif chemokine 2 (CXCL2) and C-X-C motif chemokine 6 (CXCL6). Mechanistically, DTX2 can interact with histone H2B and promote its monoubiquitination at lysine120 (H2BK120ub1), thereby increasing CXCL2 and CXCL6 transcription through histone epigenetic regulation. Different tumor models in vivo demonstrated that DTX2 inhibitor treatment inhibited tumor growth and sensitized HCC cells to the therapeutic effects of programmed cell death protein 1 (PD-1) antibody. In summary, this study identifies DTX2 as a potential target for HCC immunotherapy.
Keywords: DTX2 inhibitor; deltex E3 ubiquitin ligase 2; hepatocellular carcinoma; tumor‐associated neutrophils.
© 2024 The Author(s). Advanced Science published by Wiley‐VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures






References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 82073217/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 82073218/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 82003084/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 82273387/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 82273386/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 82403408/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 82122051/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 82073245/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 2018SHZDZX05/Science and Technology Major Project
- 2019-I2M-5-058/CIFMS
- 2018YFC1312100/National Key R&D Program of China
- 2020YFE0202200/National Key R&D Program of China
- SHDC2020CR5007/Clinical Research Plan of SHDC
- 202040221/Shanghai Municipal Health Commission
- 2023ZYYS-011/Outstanding Resident Clinical Postdoctoral Program of Zhongshan Hospital Affiliated to Fudan University
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
