RUNX2 enhances bladder cancer progression by promoting glutamine metabolism
- PMID: 39733689
- PMCID: PMC11743350
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neo.2024.101120
RUNX2 enhances bladder cancer progression by promoting glutamine metabolism
Abstract
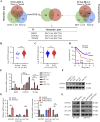
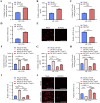
Bladder cancer is a prevalent malignancy within the urinary system. Prior research has suggested that glutamine metabolism plays a crucial role in driving bladder cancer progression. However, the precise molecular mechanism governing glutamine metabolism in bladder cancer is still inadequately understood. The research revealed a significant correlation between high levels of RUNX2 and SLC7A6 and advanced clinical stage, as well as poor prognosis, in bladder cancer patients. Furthermore, manipulating the levels of RUNX2 through overexpression or silencing demonstrated a significant impact on glutamine and bladder cancer progression. Mechanically, RUNX2 regulates the transcription of SLC7A6, resulting in enhanced glutamine metabolism and promoting the progression of bladder cancer. Overall, this research affirms the crucial function of RUNX2 as a key transcription factor to promoting glutamine and cancer development through modulation of SLC7A6. Targeting RUNX2 could represent a promising therapeutic approach for addressing aberrant glutamine metabolism in bladder cancer.
Keywords: Bladder cancer; Glutamine metabolism; RUNX2.
Copyright © 2024. Published by Elsevier Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures





References
-
- Lopez-Beltran A, Cookson MS, Guercio BJ, Cheng L. Advances in diagnosis and treatment of bladder cancer. BMJ. 2024;384 - PubMed
-
- Bray F, Laversanne M, Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2024;74:229–263. - PubMed
-
- Lobo N, Afferi L, Moschini M, Mostafid H, Porten S, Psutka SP, Gupta S, Smith AB, Williams SB, Lotan Y. Epidemiology, screening, and prevention of bladder cancer. Eur. Urol. Oncol. 2022;5:628–639. - PubMed
-
- Facchini G, Cavaliere C, Romis L, Mordente S, Facchini S, Iovane G, Capasso M, D'Errico D, Liguori C, Formato R, et al. Advanced/metastatic bladder cancer: current status and future directions. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2020;24:11536–11552. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

