Ascertainment of Small Airways Dysfunction Using Oscillometry to Better Define Asthma Control and Future Risk: Are We Ready to Implement It in Clinical Practice?
- PMID: 39734054
- PMCID: PMC12106962
- DOI: 10.1016/j.chest.2024.12.020
Ascertainment of Small Airways Dysfunction Using Oscillometry to Better Define Asthma Control and Future Risk: Are We Ready to Implement It in Clinical Practice?
Abstract
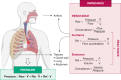
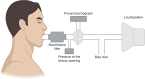
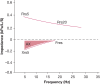
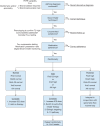
The small airways comprise generations 8 to 23 of the bronchial tree, consist of airways with an internal diameter < 2 mm, and are classically difficult to assess and treat in persistent asthma. Small airways dysfunction (SAD) is integral to the asthma management paradigm because it is associated with poorer symptom control and greater levels of type 2 inflammation, and it has been proposed as a potentially treatable asthma trait. Although identification of SAD based on oscillometry has been found to be clinically useful in managing asthma, very few physicians, including specialists, use this technique as part of standard or adjunct evaluation of lung function to diagnose asthma, grade severity of airway obstruction, ascertain disease control or the risk for future exacerbations, or to make management decisions. To rectify the unrecognized value of oscillometry in the asthma community, a consortium of authors who are investigators with knowledge and experience of oscillometry wished to address the most important clinical questions raised by our colleagues who are considering using this technique, including its clinical utility. In this article, we discuss integral concepts, including applicability of oscillometry as a predictive tool for asthma exacerbations and disease control, adequacy of spirometry and oscillometry in assessing SAD, potential limitations of oscillometry, and treatment options for SAD.
Keywords: asthma; oscillometry; small airways dysfunction.
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Financial/Nonfinancial Disclosures The authors have reported to CHEST the following: R. C. reports institutional grants from Chiesi; advisory boards for AstraZeneca; personal fees (talks) from AstraZeneca, Chiesi, and Thorasys; support for attending meetings from AstraZeneca, Chiesi, NIOX, and Sanofi-Regeneron; and honoraria (drafting educational material) from AstraZeneca and Vitalograph. L. G.-R. reports personal fees for conferences from GlaxoSmithKline, Chiesi, and Thorasys; and support for attending European Respiratory Society Congress from Chiesi. E. A. G. has received institutional grants from Gilead, Circassia, Chiesi, Propeller Health, Helicon Health, Adherium Ltd, and AstraZeneca; and personal fees from Circassia and Sanofi. F. M. D. has received unrestricted research funds from AstraZeneca, Covis Pharma, GlaxoSmithKline, Merck Canada, Novartis, Teva, Trudell Medical, GlaxoSmithKline, and MEDTEQ in partnership with Thorasys Inc; honoraria for consultancy work from AstraZeneca, Covis Pharma, Sanofi, Teva, and Thorasys Inc; and honoraria as an invited speaker from Covis Pharma, Jean-Coutu Pharmacy, and Brunet Pharmacy. None declared (M. C., P. C., S. P. G.).
Figures
References
-
- Bateman E.D., Boushey H.A., Bousquet J., et al. Can guideline-defined asthma control be achieved? The Gaining Optimal Asthma ControL study. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2004;170(8):836–844. - PubMed
-
- Cottini M., Licini A., Lombardi C., Berti A. Prevalence and features of IOS-defined small airway disease across asthma severities. Respir Med. 2021;176 - PubMed
-
- Kuo C.R., Jabbal S., Lipworth B. Is small airways dysfunction related to asthma control and type 2 inflammation? Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2018;121(5):631–632. - PubMed
-
- Cottini M., Lombardi C., Comberiati P., et al. Oscillometry defined small airways dysfunction as a treatable trait in asthma. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2025;134(2):151–158. - PubMed
-
- Cottini M., Bondi B., Bagnasco D., et al. Impulse oscillometry defined small airway dysfunction in asthmatic patients with normal spirometry: prevalence, clinical associations, and impact on asthma control. Respir Med. 2023;218 - PubMed

