Ginsenoside Ro improves Salmonella Typhimurium-induced colitis through inhibition of the virulence factors SopB and SopE2 via the RAC1/CDC42/ARP2/3 pathway
- PMID: 39734277
- PMCID: PMC11695707
- DOI: 10.1096/fj.202401712R
Ginsenoside Ro improves Salmonella Typhimurium-induced colitis through inhibition of the virulence factors SopB and SopE2 via the RAC1/CDC42/ARP2/3 pathway
Abstract
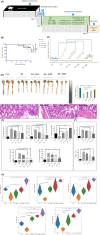
Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium (S. Typhimurium) poses a serious threat to human and animal health, and there is an urgent need to develop new therapeutic agents. In our in vivo study, ginsenoside Ro (Ro) reduced the mortality rate of S. Typhimurium-infected mice by effectively improving three key disease activity index (DAI) indicators. In particular, ginsenoside Ro inhibited S. Typhimurium-induced colitis by reversing colon length shortening; alleviating pathological damage to the colon; decreasing the levels of IL-1β, TNF-α, IFN-γ, and IL-6; and decreasing the activities of MPO and EPO, while increasing the levels of IL-10 as well as the colon epithelial barrier and tight junction-related genes (Mucin 1, Mucin 2, Occludin, Claudin-3, and ZO-1). Furthermore, ginsenoside Ro reduced CFUs in the liver, spleen, colon, and feces. In a mechanistic in vitro study, ginsenoside Ro reduced CFUs in HeLa and Raw264.7 cells, which was associated with ginsenoside Ro inhibition of the recruited S. Typhimurium-containing vacuole (SCV) biomarkers LC3, Rab7, GAL8, and NDP52. Molecular docking results revealed that the binding energies of ginsenoside Ro and SopB and ginsenoside Ro and SopE2 were as high as -11.3 and -9.7 kcal/mol, respectively, as verified by CETSA and DARTS assays. Moreover, ginsenoside Ro at 100 and 200 μM significantly decreased the enzyme activities and expression of SopB and SopE2. Finally, ginsenoside Ro inhibited the membrane ruffling caused by SopB-regulated Arf6/Cyth2/Arf1-, RAC1-, and CDC42-driven Arp2/3-dependent actin polymerization and the SopE2-regulated CDC42/Arp2/3 signaling pathway. In summary, our findings suggest that ginsenoside Ro is a potential lead compound for therapeutic use against S. Typhimurium infection, and these findings lay a foundation for its further development.
Keywords: S. Typhimurium; colitis; ginsenoside Ro; invasion; virulence factors.
© 2024 Federation of American Societies for Experimental Biology.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Dietary limonin alleviates Salmonella Typhimurium-induced colitis via dual targeting virulence SopB and SopE2 and inhibiting RAC1/CDC42/Arp2/3 pathway and regulating gut microbiota.Food Funct. 2025 Feb 3;16(3):1041-1059. doi: 10.1039/d4fo02810d. Food Funct. 2025. PMID: 39820212
-
SopB-Mediated Recruitment of SNX18 Facilitates Salmonella Typhimurium Internalization by the Host Cell.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2017 Jun 15;7:257. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2017.00257. eCollection 2017. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 28664153 Free PMC article.
-
Role of the Salmonella pathogenicity island 1 effector proteins SipA, SopB, SopE, and SopE2 in Salmonella enterica subspecies 1 serovar Typhimurium colitis in streptomycin-pretreated mice.Infect Immun. 2004 Feb;72(2):795-809. doi: 10.1128/IAI.72.2.795-809.2004. Infect Immun. 2004. PMID: 14742523 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of effector proteins translocated via the SPI1 type III secretion system of Salmonella typhimurium.Int J Med Microbiol. 2002 Feb;291(6-7):479-85. doi: 10.1078/1438-4221-00156. Int J Med Microbiol. 2002. PMID: 11890547 Review.
-
Salmonella entry into host cells: the work in concert of type III secreted effector proteins.Microbes Infect. 2001 Nov-Dec;3(14-15):1293-8. doi: 10.1016/s1286-4579(01)01489-7. Microbes Infect. 2001. PMID: 11755417 Review.
Cited by
-
Molecular mechanisms of co-infections.EMBO Rep. 2025 Aug;26(15):3714-3729. doi: 10.1038/s44319-025-00517-2. Epub 2025 Jul 4. EMBO Rep. 2025. PMID: 40615578 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 32473029/The National Nature Science Foundation of China
- 2021YFC2600200/The National Key Research and Development Program of China
- JKH20211179KJ/The Science and Technology Research Project of the Jilin Provincial Department of Education
- 2016444/The Science and Technology Research Project of the Jilin Provincial Department of Education
- 20210101341JC/Jilin Provincial Nature Science Foundation of Jilin Provincial Department of Science and Technology
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

