Exosomes derived from microRNA-540-3p overexpressing mesenchymal stem cells promote immune tolerance via the CD74/nuclear factor-kappaB pathway in cardiac allograft
- PMID: 39734479
- PMCID: PMC11669987
- DOI: 10.4252/wjsc.v16.i12.1022
Exosomes derived from microRNA-540-3p overexpressing mesenchymal stem cells promote immune tolerance via the CD74/nuclear factor-kappaB pathway in cardiac allograft
Abstract
Background: Heart transplantation is a crucial intervention for severe heart failure, yet the challenge of organ rejection is significant. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells (BMSCs) and their exosomes have demonstrated potential in modulating T cells, dendtitic cells (DCs), and cytokines to achieve immunomodulatory effects. DCs, as key antigen-presenting cells, play a critical role in shaping immune responses by influencing T-cell activation and cytokine production. Through this modulation, BMSCs and their exosomes enhance graft tolerance and prolonging survival.
Aim: To explore the immunomodulatory effects of exosomes derived from BMSCs overexpressing microRNA-540-3p (miR-540-3p) on cardiac allograft tolerance, focusing on how these exosomes modulating DCs and T cells activity through the CD74/nuclear factor-kappaB (NF-κB) pathway.
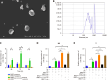
Methods: Rat models were used to assess the impact of miR-540-3p-enhanced exosomes on immune tolerance in cardiac allografts. MiR-540-3p expression was manipulated in BMSCs, and derived exosomes were collected and administered to the rat models post-heart transplantation. The study monitored expression levels of major histocompatibility complex II, CD80, CD86, and CD274 in DCs, and quantified CD4+ and CD8+ T cells, T regulatory cells, and cytokine profiles.
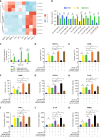
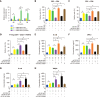
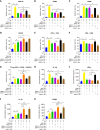
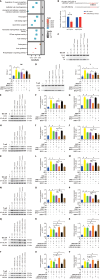
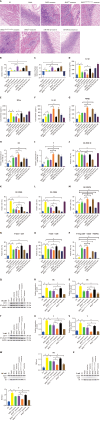
Results: Exosomes from miR-540-3p-overexpressing BMSCs lead to reduced expression of immune activation markers CD74 and NF-κB p65 in DCs and T cells. Rats treated with these exosomes showed decreased inflammation and improved cardiac function, indicated by lower levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines (interleukin-1β, interferon-γ) and higher levels of anti-inflammatory cytokines (interleukin-10, transforming growth factor β1). Additionally, miR-540-3p skewed the profiles of DCs and T cells towards immune tolerance, increasing the ratio of T regulatory cells and shifting cytokine secretion to favor graft acceptance.
Conclusion: Exosomes derived from BMSCs overexpressing miR-540-3p significantly enhance immune tolerance and prolong cardiac allograft survival by modulating the CD74/NF-κB pathway, which regulates activities of DCs and T cells. These findings highlight a promising therapeutic strategy to improve heart transplantation outcomes and potentially reduce the need for prolonged immunosuppression.
Keywords: Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells; Cardiac allograft; Exosomes; Immune tolerance; MicroRNA-540-3p.
©The Author(s) 2024. Published by Baishideng Publishing Group Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: The Yunan Labreal Biotech Ltd, co. provided the research materials in the animal experiment. Although the animal experiment was performed in the platform of a private company, they did not aware of or interfere the experimental propose and not participate in the writing, review, and publication of this manuscript. No economic interests were appeared.
Figures


References
-
- Mcdermott JK. Complications of Immunosuppression. In: Bogar L, Stempien-Otero A. Contemporary Heart Transplantation. Organ and Tissue Transplantation. Cham: Springer, 2020.
-
- Zhang X, Li M, Lian D, Zheng X, Zhang ZX, Ichim TE, Xia X, Huang X, Vladau C, Suzuki M, Garcia B, Jevnikar AM, Min WP. Generation of therapeutic dendritic cells and regulatory T cells for preventing allogeneic cardiac graft rejection. Clin Immunol. 2008;127:313–321. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

