Diabetic cardiomyopathy: pathophysiology, imaging assessment and therapeutical strategies
- PMID: 39734497
- PMCID: PMC11681223
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ijcrp.2024.200338
Diabetic cardiomyopathy: pathophysiology, imaging assessment and therapeutical strategies
Abstract
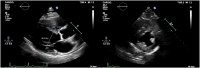
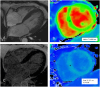
Diabetes mellitus (DM) is one of the most prevalent cardiovascular risk factors in the general population, being associated with high morbidity and socioeconomic burden. Diabetic cardiomyopathy (DCM) is a non-negligible complication of DM, whose pathophysiological fundaments are the altered cardiac metabolism, the hyperglycemia-triggered formation of advanced glycation end-products (AGEs) and the inflammatory milieu which are typical in diabetic patients. These metabolic abnormalities lead to cardiomyocytes apoptosis, interstitial fibrosis and mechanical cardiac dysfunction, which can be identified with non-invasive imaging techniques, like echocardiography and cardiac magnetic resonance. This review aims to: 1) describe the major imaging features of DCM; 2) highlight how early identification of DCM-related anatomical and functional remodeling might allow patients' therapy optimization and prognosis improvement.
Keywords: Diabetic cardiomyopathy; Heart failure; cardiac imaging; diabetes mellitus.
© 2024 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no relationships that could be construed as a conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Liu Z., Zhao N., Zhu H., Zhu S., Pan S., Xu J. Implications of underlying mechanisms for the recognition and management of diabetic cardiomyopathy. J. Diabetes Res. 2017;2017
-
- Marx N., Federici M., Schütt K., Müller-Wieland D., Ajjan R.A., Antunes M.J., et al. 2023 ESC Guidelines for the management of cardiovascular disease in patients with diabetes. Eur. Heart J. 2023;44:4043–4140.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
