Diabetic Ketoacidosis Without Diabetes Mellitus in Acute Pancreatitis
- PMID: 39734500
- PMCID: PMC11680747
- DOI: 10.1016/j.aace.2024.07.007
Diabetic Ketoacidosis Without Diabetes Mellitus in Acute Pancreatitis
Abstract
Background/objective: Diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) is typically but not exclusively seen in patients with a history of diabetes mellitus.
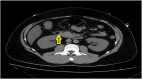
Case report: This is a case of 39 year-old male who was diagnosed with acute pancreatitis based on characteristic symptoms and positive CT findings on presentation. Laboratory testing revealed elevated serum glucose 251 mg/dL, low serum bicarbonate 8 mmol/L, increased anion gap 21, and elevated serum beta-hydroxybutyrate 9.62 mmol/L. Diagnosis of DKA was made, however patient did not carry a diagnosis of diabetes mellitus. His hemoglobin A1c in hospital was normal at 5.4%. Additionally, follow-up hemoglobin A1c at 4 months and 10 months postdischarge did not imply diabetes mellitus, 5.8% at both time points. The patient who was initially managed with intravenous insulin required no insulin or oral diabetic medication on discharge. All these findings argued against new onset diabetes mellitus.
Discussion: This case explores the potential pathophysiology that underlies this phenomenon including possible transient insulin insufficiency due to beta cell dysfunction from pancreatic inflammation. It also highlights the reversibility and transiency of possible beta cell dysfunction during acute pancreatitis and emphasizes the importance of closely assessing the patients' insulin requirements upon discharge, especially when a prior history of diabetes mellitus is absent.
Conclusion: DKA can occur as a rare complication of acute pancreatitis in a nondiabetic patient. Hyperglycemia associated with acute pancreatitis-induced DKA can be temporary and these patients might not necessarily require insulin upon discharge. Therefore, careful discharge planning is very important in such patients.
Keywords: acute pancreatitis; diabetes mellitus; siabetic ketoacidosis.
© 2024 AACE. Published by Elsevier Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Beyond Glucose Levels: Redefining Diabetic Ketoacidosis-A Case of Hypoglycemic Diabetic Ketoacidosis.AACE Clin Case Rep. 2025 Jan 11;11(2):148-150. doi: 10.1016/j.aace.2025.01.001. eCollection 2025 Mar-Apr. AACE Clin Case Rep. 2025. PMID: 40201456 Free PMC article.
-
Diabetic Ketoacidosis Complicating Gestational Diabetes Mellitus.AACE Clin Case Rep. 2022 Jul 19;8(5):221-223. doi: 10.1016/j.aace.2022.07.002. eCollection 2022 Sep-Oct. AACE Clin Case Rep. 2022. PMID: 36189139 Free PMC article.
-
Self-Induced Euglycemic Diabetic Ketoacidosis: When to Stop the Drip.Cureus. 2022 Jan 31;14(1):e21768. doi: 10.7759/cureus.21768. eCollection 2022 Jan. Cureus. 2022. PMID: 35251838 Free PMC article.
-
A new onset drug induced diabetes mellitus presenting with diabetic ketoacidosis in a child undergoing treatment for B cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. A case report and review of literature.J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 2024 Jan 29;37(4):367-370. doi: 10.1515/jpem-2023-0443. Print 2024 Apr 25. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 2024. PMID: 38281148 Review.
-
[Fulminant type 1 diabetes mellitus with acute pancreatitis: A case report and literature review].Beijing Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2024 Oct 18;56(5):923-927. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2024.05.027. Beijing Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2024. PMID: 39397476 Free PMC article. Review. Chinese.
References
-
- Euglycemic diabetic ketoacidosis with acute pancreatitis in a patient not known to have Diabetes. AACE Clin Case Rep. 2015;1:e88–e91.
-
- Prater J., Chaiban J.T. Euglycemic diabetic ketoacidosis with acute pancreatitis in a patient not known to have diabetes. AACE Clin Case Rep. 2014;1:88–91. doi: 10.4158/EP14182.CR. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous