A two-sample Mendelian randomization study reveals the causal effects of statin medication on gut microbiota abundance in the European population
- PMID: 39734574
- PMCID: PMC11674602
- DOI: 10.3389/fgene.2024.1380830
A two-sample Mendelian randomization study reveals the causal effects of statin medication on gut microbiota abundance in the European population
Abstract
Background: Observational studies have reported changes in gut microbiota abundance caused by long-term statin medication therapy. However, the causal relation between statin medication and gut microbiota subsets based on genetic variants remains unclear.
Methods: We used genome-wide association study (GWAS) data on statin medication from the FinnGen database and gut microbiota abundance GWAS data from the IEU OpenGWAS project. A Mendelian randomization (MR) analysis was conducted to evaluate the causal effect of statin medication on gut microbiota abundance using the inverse variance weighting (IVW) method, MR-Egger regression, and weighted median approach. Meanwhile, heterogeneity and pleiotropy analyses were also undertaken in this study.
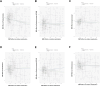
Results: Statin medication was negatively correlated with five species of gut microbiota abundance: Parabacteroides (BetaIVW = -0.2745, 95% CI = (-0.4422, -0.1068), and P IVW = 0.0013), Ruminococcaceae UCG-009 (BetaIVW = -0.1904, 95% CI = (-0.3255, -0.0553), and P IVW = 0.0057), Coprococcus 1 (BetaIVW = -0.1212, 95% CI = (-0.2194, -0.0231), and P IVW = 0.0154), Ruminococcaceae UCG-010 (BetaIVW = -0.1149, 95% CI = (-0.2238, -0.0060), and P IVW = 0.0385), and Veillonellaceae (BetaIVW = -0.0970, 95% CI = (-0.2238, 0.0060), and P IVW = 0.0400) and positively correlated with one species of gut microbiota: Desulfovibrio (BetaIVW = 0.2452, 95% CI = (0.0299, 0.4606), and P IVW = 0.0255). In addition, no significant heterogeneity or pleiotropy was detected in the abovementioned gut microbiota.
Conclusion: This Mendelian randomization analysis indicates a causal relationship between statin medication and six gut microbiota species. These findings may provide new strategies for health monitoring in populations taking long-term statin medications.
Keywords: Mendelian randomization; causal effect; gut microbiota; statin medication; two-sample Mendelian randomization.
Copyright © 2024 Zhou, Qiu, Zhuang, Shi, Yang, Ding, Qu and Xia.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Bibbins-Domingo K., Grossman D. C., Curry S. J., Davidson K. W., Epling J. W., Jr., García F. A. R., et al. (2016). Statin use for the primary prevention of cardiovascular disease in adults: US preventive services task force recommendation statement. Jama 316 (19), 1997–2007. Cited in: Pubmed; PMID 27838723. 10.1001/jama.2016.15450 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Byndloss M., Devkota S., Duca F., Hendrik Niess J., Nieuwdorp M., Orho-Melander M., et al. (2024). The gut microbiota and diabetes: research, translation, and clinical applications-2023 diabetes, diabetes care, and diabetologia expert forum. Diabetes care 47 (9), 1491–1508. Cited in: Pubmed; PMID 38996003. 10.2337/dci24-0052 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

