Lumbar Facet Joint Radiofrequency Ablation With a 3-Tined Cannula: A Technical Report and Observational Study
- PMID: 39734603
- PMCID: PMC11679272
- DOI: 10.1155/prm/8871568
Lumbar Facet Joint Radiofrequency Ablation With a 3-Tined Cannula: A Technical Report and Observational Study
Abstract
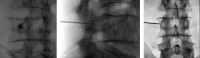
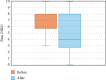
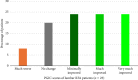
Background: Lumbar facet joints are the source of pain in 15%-41% of individuals experiencing low back pain (LBP). Conventional lumbar facet radiofrequency ablation (RFA) has Level II evidence for improving pain and function. The best proven technique, the parallel technique, is technically challenging, time-consuming, and often uncomfortable for the patient. A novel RFA technique using a 3-tined cannula offers a potentially less complex and shorter procedure. Objectives: To describe the novel lumbar facet joint RFA technique with the 3-tined cannula and to evaluate its efficacy in treating chronic lumbar facet joint pain. Methods: Eligible adult patients with chronic lumbar facet joint pain, confirmed by positive medial branch blocks (MBBs), refractory to conservative treatment, received the novel RFA treatment with the 3-tined cannula. The change in pain intensity at 2 months follow-up compared to baseline, percentage of patients reporting a ≥ 30% and ≥ 50% reduction of pain intensity, patient global impression of change (PGIC), need for pain medication, walking ability, sleep quality, and patient satisfaction were evaluated. Results: A total of 44 patients were included. Patients experienced a clinically meaningful and significant pain relief at follow-up and 41% of the patients reported ≥ 50% reduction of pain. Forty-eight percent experienced at least a score of "much improved" on the PGIC. No severe side effects or complications were observed. Conclusions: Our observational study suggests that lumbar facet joint RFA using the novel technique achieves significant pain relief. The larger lesions decrease the likelihood of missing the target nerve while obviating the need to conduct numerous lesions. Limiting is the single-center set-up with a relatively short-term follow-up duration. Randomized controlled clinical trials are warranted to confirm the efficacy of the novel RFA technique to treat lumbar facet joint pain.
Keywords: ablation; denervation; facet joint pain; low back pain; lumbar; multitined cannula; observational study; perpendicular approach; radiofrequency.
Copyright © 2024 Andrea Künzle et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Manchikanti L., Kaye A. D., Soin A., et al. Comprehensive Evidence-Based Guidelines for Facet Joint Interventions in the Management of Chronic Spinal Pain: American Society of Interventional Pain Physicians (ASIPP) Guidelines Facet Joint Interventions 2020 Guidelines. Pain Physician . 2020;23(3S):S1–S127. - PubMed
-
- Curtis L., Shah N., Padalia D. Facet Joint Disease . Treasure Island, FL: StatPearls Publishing; 2023. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

