Design of upper limb muscle strength assessment system based on surface electromyography signals and joint motion
- PMID: 39734626
- PMCID: PMC11674603
- DOI: 10.3389/fneur.2024.1470759
Design of upper limb muscle strength assessment system based on surface electromyography signals and joint motion
Abstract
Purpose: This study aims to develop a assessment system for evaluating shoulder joint muscle strength in patients with varying degrees of upper limb injuries post-stroke, using surface electromyographic (sEMG) signals and joint motion data.
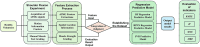
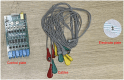
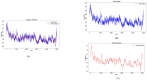
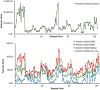
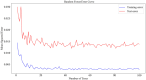
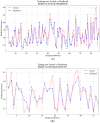
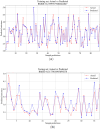
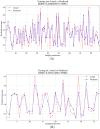
Methods: The assessment system includes modules for acquiring muscle electromyography (EMG) signals and joint motion data. The EMG signals from the anterior, middle, and posterior deltoid muscles were collected, filtered, and denoised to extract time-domain features. Concurrently, shoulder joint motion data were captured using the MPU6050 sensor and processed for feature extraction. The extracted features from the sEMG and joint motion data were analyzed using three algorithms: Random Forest (RF), Backpropagation Neural Network (BPNN), and Support Vector Machines (SVM), to predict muscle strength through regression models. Model performance was evaluated using Root Mean Squared Error (RMSE), R-Square (R 2), Mean Absolute Error (MAE), and Mean Bias Error (MBE), to identify the most accurate regression prediction algorithm.
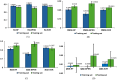
Results: The system effectively collected and analyzed the sEMG from the deltoid muscles and shoulder joint motion data. Among the models tested, the Support Vector Regression (SVR) model achieved the highest accuracy with an R 2 of 0.8059, RMSE of 0.2873, MAE of 0.2155, and MBE of 0.0071. The Random Forest model achieved an R 2 of 0.7997, RMSE of 0.3039, MAE of 0.2405, and MBE of 0.0090. The BPNN model achieved an R 2 of 0.7542, RMSE of 0.3173, MAE of 0.2306, and MBE of 0.0783.
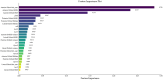
Conclusion: The SVR model demonstrated superior accuracy in predicting muscle strength. The RF model, with its feature importance capabilities, provides valuable insights that can assist therapists in the muscle strength assessment process.
Keywords: feature extraction; feature importance; muscle strength assessment; regression prediction; surface electromyographic signals; upper limb movement disorders.
Copyright © 2024 Wang, Lai, Zhang, Yao, Gou, Ye, Yi and Cao.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Development of an upper limb muscle strength rehabilitation assessment system using particle swarm optimisation.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2025 Jul 9;13:1619411. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2025.1619411. eCollection 2025. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2025. PMID: 40704098 Free PMC article.
-
Prediction of Joint Angles Based on Human Lower Limb Surface Electromyography.Sensors (Basel). 2023 Jun 7;23(12):5404. doi: 10.3390/s23125404. Sensors (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37420573 Free PMC article.
-
Application of Isokinetic Dynamometry Data in Predicting Gait Deviation Index Using Machine Learning in Stroke Patients: A Cross-Sectional Study.Sensors (Basel). 2024 Nov 13;24(22):7258. doi: 10.3390/s24227258. Sensors (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39599035 Free PMC article.
-
Neural adaptations to resistive exercise: mechanisms and recommendations for training practices.Sports Med. 2006;36(2):133-49. doi: 10.2165/00007256-200636020-00004. Sports Med. 2006. PMID: 16464122 Review.
-
Regression analysis for detecting epileptic seizure with different feature extracting strategies.Biomed Tech (Berl). 2019 Dec 18;64(6):619-642. doi: 10.1515/bmt-2018-0012. Biomed Tech (Berl). 2019. PMID: 31145684 Review.
Cited by
-
Development of an upper limb muscle strength rehabilitation assessment system using particle swarm optimisation.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2025 Jul 9;13:1619411. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2025.1619411. eCollection 2025. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2025. PMID: 40704098 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Fernández-Solana J, Álvarez-Pardo S, Moreno-Villanueva A, Santamaria-Pelíaez M, González-Bernal JJ, Vélez-Santamaría R, et al. . Efficacy of a rehabilitation program using mirror therapy and cognitive therapeutic exercise on upper limb functionality in patients with acute stroke. Healthcare. (2024) 12:569. 10.3390/healthcare12050569 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

