Factors Affecting Surgical Success Rates in Pediatric Horizontal Strabismus Surgery
- PMID: 39734963
- PMCID: PMC11682706
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.74758
Factors Affecting Surgical Success Rates in Pediatric Horizontal Strabismus Surgery
Abstract
Introduction: Horizontal strabismus is a binocular alignment disorder that can lead to significant complications in childhood, such as visual impairment and amblyopia. This study aimed to evaluate the success rates of horizontal strabismus surgery in pediatric patients and to identify the factors affecting surgical outcomes. Specifically, it examined the relationship between surgical success and factors such as age, deviation angle, and amblyopia in pediatric horizontal strabismus cases.
Methods: The medical records of 95 patients diagnosed with horizontal strabismus and treated surgically between 2016 and 2022 were reviewed. Surgical success was defined by a postoperative deviation angle of less than 10 prism diopters (PD). Visual acuity and deviation angles were measured before and after surgery, and the data were analyzed statistically.
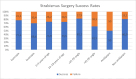
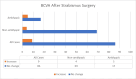
Results: Among the cases, 49 (51.5%) were diagnosed with esotropia and 46 (48.5%) with exotropia. One year after surgery, the overall success rate was recorded at 73.6%. The success rates were 77.6% in the esotropia group and 69.6% in the exotropia group, with no statistically significant difference between the groups (p=0.515). In age-based analyses, the surgical success rate was 73.8% in patients aged 0-9 years and 73.5% in those aged 10-18 years. Patients with a deviation angle greater than 45 PD had a success rate of 61.5%, while those with an angle below 45 PD achieved a success rate of 82.1% (p<0.05). Surgical success was observed in 50% of patients with amblyopia and 80.9% of those without amblyopia. Improvement in visual acuity was observed in 5.5% of non-amblyopic patients and in 22.7% of amblyopic patients; however, this improvement was not statistically correlated with surgical success.
Conclusions: This study revealed that factors such as the deviation angle and the presence of amblyopia affected the success rate of horizontal strabismus surgery. Surgical success rates did not differ significantly between esotropia and exotropia cases. Consistent with existing literature, patients with larger deviation angles and amblyopia were found to have lower surgical success rates.
Keywords: amblyopia; esotropia; exotropia; ocular motility disorders; strabismus; visual acuity.
Copyright © 2024, Yetkin et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Human subjects: Consent for treatment and open access publication was obtained or waived by all participants in this study. Institutional Review Board of the Non-Interventional Ethical Committee of the Adiyaman University Medical Faculty issued approval Number: 2022/8-21. The study was conducted in accordance with the guidelines of the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the Institutional Review Board of the Non-Interventional Ethical Committee of the Adiyaman University Medical Faculty (number: 2022/8-21, date of approval: November 15, 2022). Animal subjects: All authors have confirmed that this study did not involve animal subjects or tissue. Conflicts of interest: In compliance with the ICMJE uniform disclosure form, all authors declare the following: Payment/services info: All authors have declared that no financial support was received from any organization for the submitted work. Financial relationships: All authors have declared that they have no financial relationships at present or within the previous three years with any organizations that might have an interest in the submitted work. Other relationships: All authors have declared that there are no other relationships or activities that could appear to have influenced the submitted work.
Figures
References
-
- Amblyopia and the whole child. Birch EE, Kelly KR. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S1350946223000071 Prog Retinal Eye Res. 2023;93 - PMC - PubMed
-
- A social media listening study to understand the unmet needs and quality of life in adult and pediatric amblyopia patients. Syntosi A, Felizzi F, Bouchet C. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40123-022-00571-2. Ophthalmol Ther. 2022;11:2183–2196. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Strabismus. Gunton KB, Wasserman BN, DeBenedictis C. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pop.2015.05.006. Prim Care. 2015;42:393–407. - PubMed
-
- Global and regional prevalence of strabismus: a comprehensive systematic review and meta-analysis. Hashemi H, Pakzad R, Heydarian S, et al. https://doi.org/10.1080/09273972.2019.1604773. Strabismus. 2019;27:54–65. - PubMed
-
- The prevalence of strabismus and associated risk factors in a southeastern region of Brazil. Schaal LF, Schellini SA, Pesci LT, Galindo A, Padovani CR, Corrente JE. https://doi.org/10.1080/08820538.2016.1247176. Semin Ophthalmol. 2018;33:357–360. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources