Pulmonary Alveolar Proteinosis During Intensive Immunosuppressive Treatment for Acute Exacerbation of Interstitial Pneumonia: A Case Report and Literature Review
- PMID: 39734970
- PMCID: PMC11681919
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.74669
Pulmonary Alveolar Proteinosis During Intensive Immunosuppressive Treatment for Acute Exacerbation of Interstitial Pneumonia: A Case Report and Literature Review
Abstract
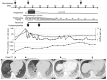
Pulmonary alveolar proteinosis (PAP) is a rare disease characterized by the accumulation of surfactants in the alveoli. It has been suggested that immunosuppressants contribute to the development and exacerbation of PAP. Here, we report the case of a 73-year-old man who developed secondary PAP after intensive immunosuppressive treatment for acute exacerbation of interstitial pneumonia (IP). In this case, despite the improvement of the inflammatory response after immunosuppressive treatment, Krebs von den Lungen-6 (KL-6) continued to increase, leading to the diagnosis of PAP. De-escalation of immunosuppressive treatment improved the PAP, allowing him to be discharged from the hospital. Although KL-6 is a useful marker of IP, when IP appears to be refractory and KL-6 increases despite the improvement of other inflammatory markers, physicians should consider the development of PAP and perform proactive bronchoscopic evaluation.
Keywords: acute exacerbation of interstitial pneumonia; immunosuppressive treatment; krebs von den lungen-6; pulmonary alveolar proteinosis; secondary pulmonary alveolar proteinosis.
Copyright © 2024, Yanagisawa et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Human subjects: Consent for treatment and open access publication was obtained or waived by all participants in this study. Conflicts of interest: In compliance with the ICMJE uniform disclosure form, all authors declare the following: Payment/services info: All authors have declared that no financial support was received from any organization for the submitted work. Financial relationships: All authors have declared that they have no financial relationships at present or within the previous three years with any organizations that might have an interest in the submitted work. Other relationships: All authors have declared that there are no other relationships or activities that could appear to have influenced the submitted work.
Figures

References
-
- Pulmonary alveolar proteinosis. Trapnell BC, Nakata K, Bonella F, et al. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2019;5:16. - PubMed
-
- Two cases of autoimmune and secondary pulmonary alveolar proteinosis during immunosuppressive therapy in dermatomyositis with interstitial lung disease. Imura Y, Yukawa N, Handa T, et al. Mod Rheumatol. 2018;28:724–729. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
