Utilization of Integrated Ayushman Bharat - Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana and Mahatma Jyotirao Phule Jan Arogya Yojana at a Tertiary Care Center in Solapur, India: An Epidemiological Study
- PMID: 39734972
- PMCID: PMC11681953
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.74680
Utilization of Integrated Ayushman Bharat - Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana and Mahatma Jyotirao Phule Jan Arogya Yojana at a Tertiary Care Center in Solapur, India: An Epidemiological Study
Abstract
Background: The Integrated Ayushman Bharat - Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana (AB-PMJAY) and Mahatma Jyotirao Phule Jan Arogya Yojana (MJPJAY) is a public-funded health insurance scheme in the state of Maharashtra. The scheme provides end-to-end cashless services for identified diseases through a network of hospitals from both the government sector as well as the private sector, covered under the scheme. AB-PMJAY is a scheme of the government of India. Such publicly funded health insurance schemes help to reduce out-of-pocket expenditure (OOPE). The study was designed with the objective of describing an epidemiological profile of subjects registered under the Integrated MJPJAY and Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana at a tertiary care center and identifying the utilization pattern of the scheme.
Methods: It was a record-based, retrospective cross-sectional study. The study population comprised all the cases registered under Integrated AB-PMJAY and MJPJAY from September 1, 2023, to November 30, 2023, at the tertiary care center. The sample size consists of all the cases (n=1978) registered under the scheme at the tertiary care center from September 1, 2023, to November 30, 2023.
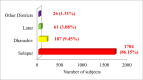
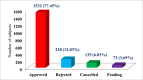
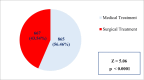
Results: The majority of the subjects (44.39%, n=878) belonged to the age group 40-59 years. In our study, 77.45% (n=1532) of the study subjects got pre-authorization approval. In the case of the pattern of utilization, 56.46% (n=865) of the study subjects utilized medical treatment, and 43.54% (n=667) of the study subjects utilized surgical treatment. In surgical treatment, utilization was higher in polytrauma (15.92%, n=244), followed by general surgery (7.70%, n=118) and ear, nose, and throat (ENT) surgery (5.68%, n=87). In the case of medical treatment, utilization was more in general medicine (14.30%, n=219), followed by nephrology (11.49%, n=176) and neurology (10.64%, n=163).
Conclusion: The majority of the subjects availing themselves of registration in the scheme were in the age group 40-59 years. The majority of the subjects utilized medical treatment. In the case of specialty utilization, polytrauma was utilized more, followed by general medicine. The utilization was least in the case of cardiothoracic surgery, followed by dermatology, hematology, and pediatric surgery.
Keywords: ayushman bharat; mjpjay; oope; out-of-pocket expenditure; pmjay; public funded health insurance; utilization pattern.
Copyright © 2024, Kolekar et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Human subjects: Consent for treatment and open access publication was obtained or waived by all participants in this study. The Institutional Ethics Committee of Dr. V. M. Government Medical College, Solapur issued approval IEC/169/24. Animal subjects: All authors have confirmed that this study did not involve animal subjects or tissue. Conflicts of interest: In compliance with the ICMJE uniform disclosure form, all authors declare the following: Payment/services info: All authors have declared that no financial support was received from any organization for the submitted work. Financial relationships: All authors have declared that they have no financial relationships at present or within the previous three years with any organizations that might have an interest in the submitted work. Other relationships: All authors have declared that there are no other relationships or activities that could appear to have influenced the submitted work.
Figures


References
-
- Ayushman Bharat and road to universal health coverage in India. Keshri VR, Gupta S. J Mahatma Gandhi Inst Med Sci. 2019;24:65–67.
-
- Universal health coverage (UHC) [ Jan; 2024 ]. 2023. https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/universal-health-covera... https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/universal-health-covera...
-
- A Study on awareness, coverage and willingness to avail health insurance among the residents of a rural area in Central Karnataka. Netra G, Rao BAV. https://njcmindia.com/index.php/file/article/view/483/296 Natl J Community Med. 2019;10:190–196.
-
- Training manual in health insurance. [ Apr; 2024 ]. 2009. https://iphindia.org/training-manual-in-health-insurance/ https://iphindia.org/training-manual-in-health-insurance/
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
