Effect of Different Cantilever Lengths in Polyether Ether Ketone Prosthetic Framework in All-on-Four Technique on Stress Distribution: A Three-Dimensional (3D) Finite Element Analysis
- PMID: 39735106
- PMCID: PMC11671772
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.74544
Effect of Different Cantilever Lengths in Polyether Ether Ketone Prosthetic Framework in All-on-Four Technique on Stress Distribution: A Three-Dimensional (3D) Finite Element Analysis
Abstract
Background: Determining the distal cantilever length in All-on-Four (All-on-4) implant-supported prostheses is a major factor in the long-term success of these prostheses. The difference in mechanical properties of materials used in the fabrication of these prostheses, such as polyether ether ketone (PEEK), may have an impact on the determination of the cantilever length that best distributes stress.
Aim: To study the distribution of stress in All-on-4 mandibular prostheses in the bone, implants, and framework according to difference cantilever length in PEEK prosthetic framework using three-dimensional finite element analysis.
Materials and methods: A three-dimensional (3D) model of an edentulous mandible was constructed, implants and abutments models were designed by the All-on-4 concept, and two frameworks were constructed from PEEK with different cantilever lengths of 10 and 15 mm. Two study groups were created. Occlusal oblique forces of 600N were applied from the right side at a 45-degree angle, and finite element analysis was performed to obtain the stress distribution in the bone, implants, and framework.
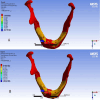
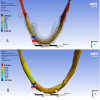
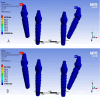
Results: At cantilever length of 10 mm, in the PEEK model, this study found an increase in stress compared to PEEK model at cantilever length of 15 mm in the cortical bone and implants and framework, but PEEK models showed a similar distribution of stress in the spongy bone.
Conclusions: Decreasing the cantilever length in the PEEK model will increase the stress. PEEK models showed deformation of the structure material.
Keywords: all on 4; cantilever length; finite element analysis; peek; stress.
Copyright © 2024, Almjaddr et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Human subjects: All authors have confirmed that this study did not involve human participants or tissue. Animal subjects: All authors have confirmed that this study did not involve animal subjects or tissue. Conflicts of interest: In compliance with the ICMJE uniform disclosure form, all authors declare the following: Payment/services info: All authors have declared that no financial support was received from any organization for the submitted work. Financial relationships: All authors have declared that they have no financial relationships at present or within the previous three years with any organizations that might have an interest in the submitted work. Other relationships: All authors have declared that there are no other relationships or activities that could appear to have influenced the submitted work.
Figures







References
-
- Quality of life of implant-supported overdenture and conventional complete denture in restoring the edentulous mandible: a systematic review. Zhang L, Lyu C, Shang Z, Niu A, Liang X. Implant Dent. 2017;26:945–950. - PubMed
-
- Biomechanical comparison of different implant inclinations and cantilever lengths in all-on-4 treatment concept by three-dimensional finite element analysis. Ozan O, Kurtulmus-Yilmaz S. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2018;33:64–71. - PubMed
-
- Applications of polyetheretherketone (PEEK) in oral implantology and prosthodontics. Najeeb S, Zafar MS, Khurshid Z, Siddiqui F. J Prosthodont Res. 2016;60:12–19. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
