Pan-Cancer Analysis of the Prognostic and Immunological Role of SEMA7A
- PMID: 39735166
- PMCID: PMC11682669
- DOI: 10.2147/IJGM.S499872
Pan-Cancer Analysis of the Prognostic and Immunological Role of SEMA7A
Abstract
Background: Semaphorin7A (SEMA7A) has been found to regulate both nerve and vessel homeostasis, but its specific role in pan-cancer remains uncertain. This research seeks to delve into the function and clinical relevance of SEMA7A in pan-cancer.
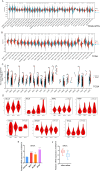
Methods: Through an analysis of gene expression omnibus and the cancer genome atlas datasets, we investigated the impact of SEMA7A on prognosis and immune regulation across 33 types of tumors. Variations in SEMA7A expression were observed between cancerous and adjacent normal tissues, with a notable correlation between SEMA7A levels and patient prognosis.
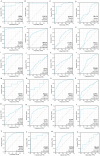
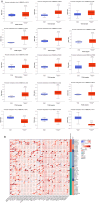
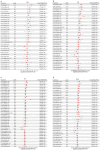
Results: Across most cancer types, SEMA7A expression was linked to the infiltration of immune cells, as well as immune checkpoints and other immune regulators. The findings were further confirmed through quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction analysis of SEMA7A expression in breast cancer. Further, SEMA7A is positively associated with prognosis in different cancers. Additionally, SEMA7A expression was associated with TMB and MSI in some cancer types, while in 15 types of cancer, there was a correlation between SEMA7A expression and DNA methylation. SEMA7A was associated with the expression of multiple immune checkpoint genes and abundance of tumor-infiltrating immune cells across multiple types of cancer.
Conclusion: This inaugural pan-cancer examination of SEMA7A sheds light on its prognostic and immunological significance in diverse tumor types, suggesting its potential utility as a biomarker for predicting unfavorable outcomes and immune cell infiltration in cancer.
Keywords: SEMA7A; immune cell infiltration; pan-cancer; prognosis.
© 2024 Yang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

