Assuring assistance to healthcare and medicine: Internet of Things, Artificial Intelligence, and Artificial Intelligence of Things
- PMID: 39735232
- PMCID: PMC11671483
- DOI: 10.3389/frai.2024.1442254
Assuring assistance to healthcare and medicine: Internet of Things, Artificial Intelligence, and Artificial Intelligence of Things
Abstract
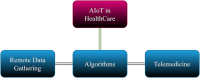
Introduction: The convergence of healthcare with the Internet of Things (IoT) and Artificial Intelligence (AI) is reshaping medical practice with promising enhanced data-driven insights, automated decision-making, and remote patient monitoring. It has the transformative potential of these technologies to revolutionize diagnosis, treatment, and patient care.
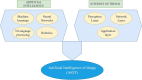
Purpose: This study aims to explore the integration of IoT and AI in healthcare, outlining their applications, benefits, challenges, and potential risks. By synthesizing existing literature, this study aims to provide insights into the current landscape of AI, IoT, and AIoT in healthcare, identify areas for future research and development, and establish a framework for the effective use of AI in health.
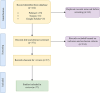
Method: A comprehensive literature review included indexed databases such as PubMed/Medline, Scopus, and Google Scholar. Key search terms related to IoT, AI, healthcare, and medicine were employed to identify relevant studies. Papers were screened based on their relevance to the specified themes, and eventually, a selected number of papers were methodically chosen for this review.
Results: The integration of IoT and AI in healthcare offers significant advancements, including remote patient monitoring, personalized medicine, and operational efficiency. Wearable sensors, cloud-based data storage, and AI-driven algorithms enable real-time data collection, disease diagnosis, and treatment planning. However, challenges such as data privacy, algorithmic bias, and regulatory compliance must be addressed to ensure responsible deployment of these technologies.
Conclusion: Integrating IoT and AI in healthcare holds immense promise for improving patient outcomes and optimizing healthcare delivery. Despite challenges such as data privacy concerns and algorithmic biases, the transformative potential of these technologies cannot be overstated. Clear governance frameworks, transparent AI decision-making processes, and ethical considerations are essential to mitigate risks and harness the full benefits of IoT and AI in healthcare.
Keywords: AI; AIoT; IOT in medicine; LLMS; deep learning and NLP; machine learning.
Copyright © 2024 Belbase, Bhusal, Ghimire, Sharma and Banskota.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted without any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Al-kfairy M., Mustafa D., Kshetri N., Insiew M., Alfandi O. (2024). Ethical challenges and solutions of generative AI: An interdisciplinary perspective. Informatics. 11:58. doi: 10.3390/informatics11030058 - DOI
-
- Anurag Moosavi SR, Rahmani AM, Westerlund T, Yang G, Liljeberg P, et al. Pervasive health monitoring based on internet of things: two case studies. Proceedings of the 2014 4th International Conference on Wireless Mobile Communication and Healthcare - "Transforming Healthcare through Innovations in Mobile and Wireless Technologies", Mobihealth 2014. (2015). 275–278.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources