Spontaneous Pneumocephalus associated with leptomeningeal glioneuronal tumor in an adult; A rare case report
- PMID: 39735235
- PMCID: PMC11681790
- DOI: 10.1016/j.joto.2024.07.004
Spontaneous Pneumocephalus associated with leptomeningeal glioneuronal tumor in an adult; A rare case report
Abstract
Objective: To report a rare case of otogenic tension pneumocephalus as a complication of a diffuse leptomeningeal glioneuronal tumor in a patient with a ventriculoperitoneal (V. P.) shunt.
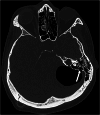
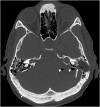
Patients: Twenty-three- year-old man with a confirmed diffuse leptomeningeal glioneuronal tumor diagnosis was treated for temporal bone defect and considerable pneumocephalus one year after V. P. shunt.
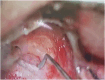
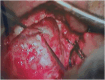
Interventions: The patient underwent a Transmastoid, retrolabyrinthine approach. The defect was closed with temporalis facia graft and conchal cartilage as a double-layer closure, and then DuraSeal® was placed over the repaired area.
Main outcome measures: Resolution of the pneumocephalus.
Results: There was a significant reduction in the pneumocephalus on the first day post-operatively.
Conclusions: Spontaneous or secondary pneumocephalus development should be considered in patients with brain tumors, hydrocephalus, and patients who undergo V.P. shunt insertion.
Keywords: Leptomeningeal; Neurotology; Pneumocephalus.
© [copyright 2024] PLA General Hospital Department of Otolaryngology Head and Neck Surgery. Production and hosting by Elsevier (Singapore) Pte Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

References
-
- Aoyama I., et al. Pneumocephalus associated with benign brain tumor: report of two cases. Surg. Neurol. 1991;36(1):32–36. - PubMed
-
- Chan E.K., Meiteles L.Z. Otogenic tension pneumocephalus caused by therapeutic lumbar CSF drainage for post-traumatic hydrocephalus: a case report. Ear Nose Throat J. 2007;86(7):391–405. - PubMed
-
- Dandy W. Pneumatoceles (intracranial pneumatocele or aerocele) Arch. Surg. 1926;12:949–982.
-
- Hage P., et al. Spontaneous otogenic pneumocephalus due to altitude changes: a case report and review of literature. Clin. Neurol. Neurosurg. 2015;138:162–164. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

