Preliminary study of the role of inner ear proteins in vestibular neuritis
- PMID: 39735237
- PMCID: PMC11681792
- DOI: 10.1016/j.joto.2024.04.003
Preliminary study of the role of inner ear proteins in vestibular neuritis
Abstract
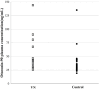
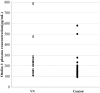
Objective: To evaluate the plasma levels of the otoconial proteins, otoconin-90 and otolin-1, in individuals diagnosed with vestibular neuritis (VN) and determine the feasibility of using these proteins as biomarkers for VN.
Methods: In this preliminary study, 30 patients diagnosed with VN and 70 healthy individuals were recruited and followed to confirm whether they had benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (BPPV) during the following time. The recorded data included measurements of height, weight, and history of diabetes mellitus or hypertension. Additionally, levels of plasma otoconin-90, and otolin-1 were measured and compared.
Results: The plasma concentrations of otoconin-90 and otolin-1 may not be significantly different between patients with VN and healthy controls, nor among patients with BPPV secondary to VN and patients with VN without BPPV.
Conclusions: Plasma otoconin-90 and otolin-1 levels may not serve as biomarkers of acute VN episodes or predict BPPV occurrence secondary to VN.
Keywords: Inner ear protein; Otoconin-90; Otolin-1; Vestibular neuritis.
© [copyright 2024] PLA General Hospital Department of Otolaryngology Head and Neck Surgery. Production and hosting by Elsevier (Singapore) Pte Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors have no potential conflicts of interest to be disclosed.
Figures
References
-
- Bhattacharyya N., Gubbels S.P., Schwartz S.R., Edlow J.A., El-Kashlan H., Fife T., Holmberg J.M., Mahoney K., Hollingsworth D.B., Roberts R., Seidman M.D., Steiner R.W.P., Do B.T., Voelker C.C.J., Waguespack R.W., Corrigan M.D. Clinical practice guideline: benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (update) Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2017;156:S1–S47. doi: 10.1177/0194599816689667. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Feng M., Zhuang J., Gu H., Tian Q., Zhang Z. Changes of serum E2 and Otolin-1 levels in postmenopausal women with BPPV. Journal of Clinical Otorhinolaryngology Head and Neck Surgery. 2019;33:1138–1141+1147. https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/42.1764.R.20191126.1359.006.html - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources