Loss of Fascin2 increases susceptibility to cisplatin-induced hearing impairment and cochlear cell apoptosis in mice
- PMID: 39735238
- PMCID: PMC11681795
- DOI: 10.1016/j.joto.2024.07.001
Loss of Fascin2 increases susceptibility to cisplatin-induced hearing impairment and cochlear cell apoptosis in mice
Abstract
Objectives: Deletion of Fscn2 gene in mice has been linked to progressive hearing loss and degeneration of cochlear cells. Cisplatin, an antitumor drug, can cause various side effects, including ototoxicity. The aim of this study was to investigate the effects of Fscn2 on cisplatin-induced hearing impairment in mice and to explore the possible mechanism.
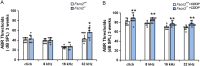
Methods: Two-week-old Fscn2 +/+ mice and Fscn2 -/- mice were treated with two doses of cisplatin, with a 3-day recovery period in between. ABR (auditory evoked brain stem response) thresholds were measured and cochlear pathology was observed at 3 weeks of age.
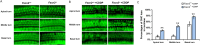
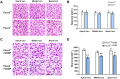
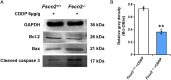
Results: Both Fscn2 +/+ and Fscn2 -/- mice showed hearing loss under the effect of cisplatin, but the impairment was more severe in Fscn2 -/- mice. Further experiments showed that the percentages of outer hair cell (OHC) and spiral ganglion neuron (SGN) loss were significantly higher in cisplatin-treated Fscn2 -/- mice compared to Fscn2 +/+ mice. Additionally, knockdown of Fscn2 in HEI-OC1 cells worsened cisplatin-induced cell apoptosis.
Conclusion: FSCN2 mediates reduction of CDDP induced ototoxicity by inhibiting cell apoptosis.
Keywords: Apoptosis; Cisplatin; Fascin2; Mouse; Ototoxicity.
© [copyright 2024] PLA General Hospital Department of Otolaryngology Head and Neck Surgery. Production and hosting by Elsevier (Singapore) Pte Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest. The authors alone are responsible for the content and writing of the paper.
Figures

References
-
- Abercrombie M., Johnson M.L. Quantitative histology of Wallerian degeneration: I. Nuclear population in rabbit sciatic nerve. J. Anat. 1946;80:37–50. - PubMed
-
- Guillery R.W. On counting and counting errors. J. Comp. Neurol. 2002;447:1–7. - PubMed
-
- Hashimoto Y., Kim D.J., Adams J.C. The roles of fascins in health and disease. J. Pathol. 2011;224:289–300. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

