The effect of right versus left long-term single-sided deafness on sound source localization
- PMID: 39735241
- PMCID: PMC11681791
- DOI: 10.1016/j.joto.2024.02.002
The effect of right versus left long-term single-sided deafness on sound source localization
Abstract
Purpose: To analyze the effect of right versus left long-term single-sided deafness (SSD) on sound source localization (SSL), discuss the necessity of intervention and treatment for SSD patients, and analyze the therapeutic effect of long-term unilateral cochlear implantation (UCI) from the perspective of SSL.
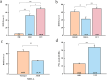
Methods: This study included 25 patients with SSD, 11 patients with UCI, and 30 participants with normal hearing (NH). Their SSL ability was tested by obtaining their average root mean square (RMS) error values of SSL test.
Results: The results showed that the RMS error value of SSD, UCI and NH groups were 52.26 ± 20.25°, 69.84 ± 12.14° and 4.27 ± 2.66°, respectively. The ability of SSL was better in the SSD-L group than that in the SSD-R group, and no significant difference existed in the SSD-R and the UCI group.
Conclusion: When bilateral deafness patients select unilateral treatment, right-side cochlear implantation may be more beneficial in terms of SSL, which means that the central auditory cortex in long-term SSD patients is affected differently based on which side their deafness occurs.
Keywords: Cochlear implantation; Single-sided deafness; Sound source localization; Treatment.
© [copyright 2024] PLA General Hospital Department of Otolaryngology Head and Neck Surgery. Production and hosting by Elsevier (Singapore) Pte Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declared no potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Sound Source Localization and Speech Understanding in Complex Listening Environments by Single-sided Deaf Listeners After Cochlear Implantation.Otol Neurotol. 2015 Sep;36(9):1467-71. doi: 10.1097/MAO.0000000000000841. Otol Neurotol. 2015. PMID: 26375967 Free PMC article.
-
Cochlear Implantation in Children With Single-Sided Deafness: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.JAMA Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2021 Jan 1;147(1):58-69. doi: 10.1001/jamaoto.2020.3852. JAMA Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2021. PMID: 33151295 Free PMC article.
-
[Analysis of one-year outcomes after cochlear implantation in adults with single-sided deafness].Zhonghua Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2024 Jun 7;59(6):602-613. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn115330-20231113-00202. Zhonghua Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2024. PMID: 38965850 Chinese.
-
Cortical reorganization after cochlear implantation for adults with single-sided deafness.PLoS One. 2018 Sep 24;13(9):e0204402. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0204402. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 30248131 Free PMC article.
-
Duration of unilateral auditory deprivation is associated with reduced speech perception after cochlear implantation: A single-sided deafness study.Cochlear Implants Int. 2019 Mar;20(2):51-56. doi: 10.1080/14670100.2018.1550469. Epub 2018 Nov 28. Cochlear Implants Int. 2019. PMID: 30486762 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

