Diagnostic and prognostic values of NSCLC patients with or without obstructive pneumonia after sleeve lobectomy
- PMID: 39735257
- PMCID: PMC11682716
- DOI: 10.3389/fcimb.2024.1474998
Diagnostic and prognostic values of NSCLC patients with or without obstructive pneumonia after sleeve lobectomy
Abstract
Objective: We aimed to identify the diagnostic value of next-generation sequencing (NGS) of bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF) from patients with non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC).
Methods: Forty patients who were initially diagnosed with pulmonary nodules were enrolled. Frozen section histology was used to identify the NSCLC cell types. NGS of collected BALF samples was used for microbial identification. We compared the bacterial and viral distributions in BALF samples from patients with NSCLC with and without obstructive pneumonia as well as their NSCLC drainage times following surgery.
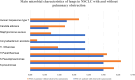
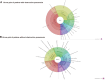
Results: Of the 29 patients with NSCLC, eight had obstructive pneumonia. Streptococcus pneumoniae, Streptococcus pseudopneumoniae, and Haemophilus parainfluenzae were the top three bacteria present in almost 50% of patients, both with and without obstructive pneumonia. The viral detection rate was higher in the BALF of patients with NSCLC who did not have obstructive pneumonia. However, in patients with NSCLC and drain times of >5 days, the human herpes virus type 7 detection rate was higher following surgery than it was in patients with NSCLC who had drain times of ≤5 days.
Conclusion: Viral imbalance in NSCLC is closely related to the occurrence of obstructive pneumonia and postoperative drainage time.
Keywords: bronchoalveolar lavage fluid; lung resection; next-generation sequencing; non-small-cell lung cancer; obstructive pneumonia.
Copyright © 2024 Huang, Zhang, Zhang, Lv and Wang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Diagnostic value of metagenomic next-generation sequencing using bronchoalveolar lavage fluid samples for pathogen detection in children with severe or refractory pneumonia.Microbiol Spectr. 2025 Mar 4;13(3):e0108724. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.01087-24. Epub 2025 Feb 4. Microbiol Spectr. 2025. PMID: 39902982 Free PMC article.
-
The clinical significance of simultaneous detection of pathogens from bronchoalveolar lavage fluid and blood samples by metagenomic next-generation sequencing in patients with severe pneumonia.J Med Microbiol. 2021 Jan;70(1). doi: 10.1099/jmm.0.001259. J Med Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 33231537
-
The Application of Metagenomic Next-Generation Sequencing in Detection of Pathogen in Bronchoalveolar Lavage Fluid and Sputum Samples of Patients with Pulmonary Infection.Comput Math Methods Med. 2021 Nov 8;2021:7238495. doi: 10.1155/2021/7238495. eCollection 2021. Comput Math Methods Med. 2021. PMID: 34790254 Free PMC article.
-
High utility of bronchoalveolar lavage fluid metagenomic next-generation sequencing approach for etiological diagnosis of pneumonia.BMC Infect Dis. 2024 Nov 2;24(1):1232. doi: 10.1186/s12879-024-10108-6. BMC Infect Dis. 2024. PMID: 39488700 Free PMC article.
-
Outcomes of lobectomy on pulmonary function for early stage non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).Thorac Cancer. 2020 Jul;11(7):1784-1789. doi: 10.1111/1759-7714.13445. Epub 2020 May 6. Thorac Cancer. 2020. PMID: 32374491 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical