Study protocol: A national cross-sectional study on psychology and behavior investigation of Chinese residents in 2023
- PMID: 39735279
- PMCID: PMC11671216
- DOI: 10.1002/hcs2.125
Study protocol: A national cross-sectional study on psychology and behavior investigation of Chinese residents in 2023
Abstract
Introduction: This study protocol specifies the primary research line and theoretical framework of the 2023 Survey of the Psychology and Behavior of the Chinese Population. It aims to establish a consistent database of Chinese residents' psychological and behavioral surveys through multi-center and large-sample cross-sectional surveys to provide robust data support for developing research in related fields. It will track the public's physical and psychological health more comprehensively and systematically.
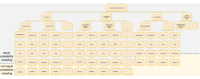
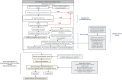
Methods: The study was conducted from June 20, 2023 to August 31, 2023, using stratified and quota sampling methods. A total of 150 cities across 800 communities/villages were surveyed, selected from China (Despite extensive coordination, we have been unable to contact our counterparts in the Taiwan region of China to obtain relevant statistical data). The questionnaires were distributed to the public one-on-one and face-to-face by trained surveyors. The questionnaires included basic information about the individual, personal health status, basic information about the family, the social environment in which the individual lives, psychological condition scales, behavioral level scales, other scales, and attitudes towards topical social issues. Supervisors conducted quality control during the distribution process and returned questionnaires, logically checked and cleaned for data analysis.
Discussion: Data collection has been finished, and scientific outputs based on this data will support the development of health promotion strategies in China and globally. In the aftermath of the pandemic, it will guide policymakers and healthcare organizations to improve their existing policies and services to maximize the physical and mental health of the Chinese population.
Trial registration: This study was filed in the National Health Security Information Platform (Record No.: MR-37-23-017876) and officially registered in the China Clinical Trials Registry (Registration No.: ChiCTR2300072573).
Keywords: Chinese residents; cross‐sectional study; health behavior; physical and psychological health.
© 2024 The Author(s). Health Care Science published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of Tsinghua University Press.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The need for holistic, longitudinal and comparable, real-time assessment of the emotional, behavioral and societal impact of the COVID-19 pandemic across nations.Psychiatriki. 2021 Apr 19;32(1):15-18. doi: 10.22365/jpsych.2021.010. Epub 2021 Mar 8. Psychiatriki. 2021. PMID: 33759804 English, Greek, Modern.
-
Residents' Awareness of Family Doctor Contract Services, Status of Contract with a Family Doctor, and Contract Service Needs in Zhejiang Province, China: A Cross-Sectional Study.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2019 Sep 9;16(18):3312. doi: 10.3390/ijerph16183312. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2019. PMID: 31505783 Free PMC article.
-
A short, animated video to improve good COVID-19 hygiene practices: a structured summary of a study protocol for a randomized controlled trial.Trials. 2020 Jun 3;21(1):469. doi: 10.1186/s13063-020-04449-1. Trials. 2020. PMID: 32493460 Free PMC article.
-
Development and evaluation of a de-escalation training intervention in adult acute and forensic units: the EDITION systematic review and feasibility trial.Health Technol Assess. 2024 Jan;28(3):1-120. doi: 10.3310/FGGW6874. Health Technol Assess. 2024. PMID: 38343036 Free PMC article.
-
Relationship between staff and quality of care in care homes: StaRQ mixed methods study.Health Soc Care Deliv Res. 2024 Apr;12(8):1-139. doi: 10.3310/GWTT8143. Health Soc Care Deliv Res. 2024. PMID: 38634535
Cited by
-
Subthreshold anxiety in Chinese college students: prevalence, gender differences, and correlates.BMC Psychol. 2025 Jul 17;13(1):803. doi: 10.1186/s40359-025-03084-2. BMC Psychol. 2025. PMID: 40676708 Free PMC article.
-
The association between bedtime smartphone use and anxiety symptoms: a network analysis of Chinese residents.BMC Psychiatry. 2025 May 26;25(1):545. doi: 10.1186/s12888-025-06961-7. BMC Psychiatry. 2025. PMID: 40420022 Free PMC article.
-
Childlessness and its associated factors among Chinese women: a nationwide population-based study.BMC Public Health. 2025 Feb 17;25(1):638. doi: 10.1186/s12889-025-21829-x. BMC Public Health. 2025. PMID: 39962454 Free PMC article.
-
Factors associated with patient privacy concerns in AI-based health monitoring devices among nursing students: a cross-sectional study.BMC Nurs. 2025 Jul 1;24(1):726. doi: 10.1186/s12912-025-03453-7. BMC Nurs. 2025. PMID: 40598528 Free PMC article.
-
Mediating effects of self-esteem and self-compassion on the relationship between body dissatisfaction and depression among adolescents with polycystic ovary syndrome.Front Public Health. 2024 Jul 25;12:1420532. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2024.1420532. eCollection 2024. Front Public Health. 2024. PMID: 39118976 Free PMC article.
References
-
- World Health Organization . Mental health[Internet]. 2022. [cited 2023 Sept 8]. World Health Organization. Available from: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/mental-health-strengthe...
-
- World Health Organization . Health and Well‐Being[Internet]. 2023. [cited 2023 Sept 8]. World Health Organization. Available from: https://www.who.int/data/gho/data/major-themes/health-and-well-being
-
- World Health Organization . World mental health report: Transforming mental health for all[Internet]. 2022. [cited 2024 July 15]. World Health Organization. Available from: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240049338
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
