Hydrogel systems for spatiotemporal controlled delivery of immunomodulators: engineering the tumor immune microenvironment for enhanced cancer immunotherapy
- PMID: 39735340
- PMCID: PMC11681625
- DOI: 10.3389/fcell.2024.1514595
Hydrogel systems for spatiotemporal controlled delivery of immunomodulators: engineering the tumor immune microenvironment for enhanced cancer immunotherapy
Abstract
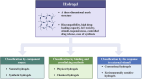
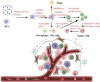
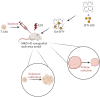
Tumor immunotherapy, modulating innate and adaptive immunity, has become an important therapeutic strategy. However, the tumor immune microenvironment's (TIME) complexity and heterogeneity challenge tumor immunotherapy. Hydrogel is a hydrophilic three-dimensional (3D) mesh structure with good biocompatibility and drug release control, which is widely used in drug delivery, agriculture, industry, etc. Hydrogels loaded with immune cells, cytokines, immune checkpoint inhibitors, and anti-tumor drugs can achieve targeted delivery and ultimately activate the immune response in the TIME. In this review, we will summarize the components of the TIME and their immune effects, the emerging immunomodulatory agents, the characteristics and functions of hydrogels, and how hydrogels regulate innate and adaptive immune cells in the TIME.
Keywords: adaptive immunity; hydrogel; immunomodulator; innate immunity; tumor immune microenvironment.
Copyright © 2024 Liu, Liu, Zeng, Lin, Yu, Zhang and Yang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

