Effects of Gynura procumbens extract supplementation on growth performance, carcass traits, antioxidant capacity, immunity and meat quality of meat ducks
- PMID: 39735580
- PMCID: PMC11671499
- DOI: 10.3389/fvets.2024.1508048
Effects of Gynura procumbens extract supplementation on growth performance, carcass traits, antioxidant capacity, immunity and meat quality of meat ducks
Abstract
Introduction: Gynura procumbens (Lour.) Merr is a common traditional Chinese medicine with anti-tumor, anti-inflammatory and antioxidant activities. However, no related studies reported the potential application effect of Gynura procumbens on meat ducks. The study aims to investigate the potential effects of Gynura procumbens extract (GPE) supplementation on growth performance, carcass traits, antioxidant capacity, immunity and meat quality.
Methods: A total of 480 21-day-old female healthy ducks were randomly allocated to four treatments, each treatment containing six replicates with 20 ducks per replicate. The groups received a corn-soybean basal diet supplemented with 0 mg/kg GPE (CON), 200 mg/kg GPE (GPE200), 400 mg/kg GPE (GPE400), and 600 mg/kg GPE (GPE600), respectively. The entire experiment lasted for 7 weeks.
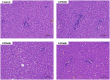
Results: The results showed that dietary supplementation with 600 mg/kg GPE significantly reduced the contents of serum urea nitrogen, triglyceride (TG) and total cholesterol (TC). GPE (200, 400, and 600 mg/kg) supplementation effectively reduced the contents of IL-2 and MDA. The levels of immunoglobulin M (IgM) as well as total antioxidative capacity (T-AOC) in GPE600 group dramatically elevated in comparison with the control group. Dietary GPE supplementation considerably increased the moisture content of the breast muscle. Furthermore, dietary supplementation with GPE markedly decreased the water loss rate and shear force.
Discussion: With the ban of antibiotics in poultry production, traditional Chinese medicines have been widely used in livestock and poultry production due to their high efficiency and low toxicity. Gynura procumbens extract GPE as a natural plant origin contains a series of biologically active components, including flavonoids, polyphenols, saponin, tannin and terpenoid. This study indicated that dietary supplementation with GPE can increase serum total antioxidant capacity, regulate immune function and improve meat quality to some extent in meat ducks. The recommended optimal GPE level in the diet of meat ducks is 600 mg/kg according to the results in this study.
Keywords: Gynura procumbens extract; antioxidant capacity; immunity; meat ducks; meat quality.
Copyright © 2024 Ai, Xiong, Chen, Song, Song, Xu, Su, Zou, Wei and Chen.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effects of rosemary extract supplementation in feed on growth performance, meat quality, serum biochemistry, antioxidant capacity, and immune function of meat ducks.Poult Sci. 2023 Feb;102(2):102357. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2022.102357. Epub 2022 Nov 19. Poult Sci. 2023. PMID: 36502565 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Dietary Zinc on Carcass Traits, Meat Quality, Antioxidant Status, and Tissue Zinc Accumulation of Pekin Ducks.Biol Trace Elem Res. 2019 Jul;190(1):187-196. doi: 10.1007/s12011-018-1534-4. Epub 2018 Oct 20. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2019. PMID: 30343482
-
Effects of grape seed extract on performance, immunity, antioxidant capacity, and meat quality in Pekin ducks.Poult Sci. 2020 Apr;99(4):2078-2086. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2019.12.014. Epub 2020 Feb 25. Poult Sci. 2020. PMID: 32241493 Free PMC article.
-
Dietary Supplementation with Phytase and Protease Improves Growth Performance, Serum Metabolism Status, and Intestinal Digestive Enzyme Activities in Meat Ducks.Animals (Basel). 2020 Feb 8;10(2):268. doi: 10.3390/ani10020268. Animals (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32046261 Free PMC article.
-
Current Knowledge Regarding Pharmacological Profile and Chemical Constituents of Gynura procumbens.Curr Top Med Chem. 2021;21(29):2671-2686. doi: 10.2174/1568026621666211004094902. Curr Top Med Chem. 2021. PMID: 34607545 Review.
References
-
- Gul ST, Alsayeqh AF. Probiotics improve physiological parameters and meat production in broiler chicks. Int J Vet Sci. (2023) 12:182–91. doi: 10.47278/journal.ijvs/2022.191 - DOI
-
- Coniglio M, Luna M, Provensal P, Watson S, Ortiz M, Ludueña H, et al. . Use of the probiotic Saccharomyces cerevisiae var. boulardii RC009 in the rearing stage of calves. Int J Agricult Biosci. (2023) 12:188–92. doi: 10.47278/journal.ijab/2023.063 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous