A Preliminary Study on Transcriptional Regulation of SNP Site C-1888T in the Promoter Region of Human PLUNC Gene and Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma Susceptibility
- PMID: 39735594
- PMCID: PMC11671629
- DOI: 10.1155/genr/5148918
A Preliminary Study on Transcriptional Regulation of SNP Site C-1888T in the Promoter Region of Human PLUNC Gene and Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma Susceptibility
Abstract
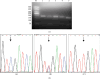
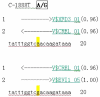
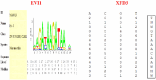
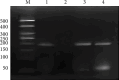
Purpose: The transcriptional regulatory factors binding to the polymorphic site C-1888T in the promoter region of the palate, lung, and nasal epithelium clone (PLUNC) gene were identified to investigate whether the C-1888T polymorphic site affects the transcriptional regulation and function of PLUNC gene. Materials and Methods: Three genotypes of C-1888T polymorphic locus were screened from established nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC) cells, and the mRNA expression levels of PLUNC gene in different genotypes were detected. The respective transcription factors that were more likely to bind with A or G in SNP were predicted by biological information and preliminarily verified in vitro by gel electrophoresis migration rate analysis. Ulteriorly, the NPC cell lines were analyzed through chromatin immunoprecipitation combined with PCR amplification to confirm that the transcription factors could bind to the PLUNC gene promoter. Results: The cell lines 5-8F, 6-10B, CNE1, and CNE2 were heterozygous CT type, SUNE1 was homozygous CC type, and C666-1 was homozygous TT type. The expression of PLUNC gene was significantly different among all cell lines (F = 33.844, p < 0.001), and the gene expression level of CC type was significantly lower than TT type (p < 0.001). Gel electrophoresis mobility analysis confirmed that the transcription factors XFD3 and EVI1 could bind to the PLUNC gene promoter when the SNP was A and G, respectively. PCR amplification combined with chromatin immunoprecipitation showed that EVI1 could bind to the DNA fragment of the promoter region of PLUNC gene in SUNE1 NPC cells. Conclusion: The transcription factors XFD3 and EVI1 may be involved in the transcriptional regulation of PLUNC gene, and EVI1 can bind to the promoter region of PLUNC gene in SUNE1 NPC cells, thus associated with the susceptibility/risk of NPC.
Keywords: PLUNC genes; nasopharyngeal carcinoma; single-nucleotide polymorphism; transcriptional regulation.
Copyright © 2024 Beina Liu et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Paredes-Durán L. M., Del Barco-Morillo E., Baldeón-Conde M. J., Medina-Valdivieso S., Guillen-Sacoto M. C., Cruz-Hernández J. J. Familial Clustering of Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma in Non-Endemic Area. Report of Three Families. Acta Otorrinolaringológica Española . 2017;68(3):164–168. doi: 10.1016/j.otorri.2016.07.006. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

