Association of circulating adiponectin and leptin levels with the risk of diabetic peripheral neuropathy
- PMID: 39735639
- PMCID: PMC11671245
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1505082
Association of circulating adiponectin and leptin levels with the risk of diabetic peripheral neuropathy
Abstract
Background: Adipokines have been implicated in the pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) and related complications due to their roles in metabolic regulation and inflammation. However, the relationship between these adipokines and diabetic peripheral neuropathy (DPN) remains unclear.
Methods: A case-control study was performed with 198 patients with DPN and 205 T2DM patients without DPN from the Endocrinology Department at the Second Affiliated Hospital of Hainan Medical University. Circulating adiponectin and leptin levels were quantified via enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays. Logistic regression models, adjusting for age, sex, BMI, smoking status, and diabetes duration, were applied to evaluate the associations between adiponectin and leptin levels and DPN risk.
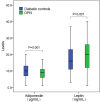
Results: DPN patients exhibited lower adiponectin (P=0.001) and higher leptin (P=0.007) levels than diabetic controls. Confounders-adjusted analyses revealed that higher adiponectin levels correlated with reduced DPN risk (OR, tertile 3 vs. tertile 1: 0.52; 95% CI: 0.30-0.90), whereas elevated leptin levels were linked to increased DPN risk (OR, tertile 3 vs. tertile 1: 1.91; 95% CI: 1.10-3.32). Stratified analyses confirmed consistent findings across subgroups without statistically significant interactions.
Conclusions: Circulating adiponectin and leptin levels correlate with DPN risk in diabetic patients, suggesting their potential as biomarkers for high-risk DPN identification and guiding targeted prevention and management.
Keywords: adiponectin; association; case-control study; diabetic peripheral neuropathy; leptin.
Copyright © 2024 Chen, Fu, Lai, Fu and Du.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Serum Adiponectin Levels Are Positively Associated With Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy in Chinese Patients With Type 2 Diabetes.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2020 Nov 25;11:567959. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2020.567959. eCollection 2020. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2020. PMID: 33324342 Free PMC article.
-
Association of serum adipocytokine levels with cardiac autonomic neuropathy in type 2 diabetic patients.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2012 Mar 13;11:24. doi: 10.1186/1475-2840-11-24. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2012. PMID: 22413919 Free PMC article.
-
Correlation between lipoprotein-associated phospholipase A2 and diabetic peripheral neuropathy in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A cross-sectional study.J Diabetes Complications. 2025 Feb;39(2):108950. doi: 10.1016/j.jdiacomp.2025.108950. Epub 2025 Jan 14. J Diabetes Complications. 2025. PMID: 39817931
-
Association between serum uric acid levels and diabetic peripheral neuropathy in type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024 Jul 12;15:1416311. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1416311. eCollection 2024. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 39072278 Free PMC article.
-
Associations of serum low-density lipoprotein and systolic blood pressure levels with type 2 diabetic patients with and without peripheral neuropathy: systemic review, meta-analysis and meta-regression analysis of observational studies.BMC Endocr Disord. 2019 Nov 25;19(1):125. doi: 10.1186/s12902-019-0453-5. BMC Endocr Disord. 2019. PMID: 31767009 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous