Relationship between triglyceride glucose-body mass index and coronary artery calcium score in maintenance hemodialysis patients
- PMID: 39735705
- PMCID: PMC11671265
- DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2024.1478090
Relationship between triglyceride glucose-body mass index and coronary artery calcium score in maintenance hemodialysis patients
Abstract
Background: This study investigated the association between coronary artery calcification (CAC) and triglyceride glucose-body mass index (TyG-BMI) in patients receiving maintenance hemodialysis (MHD).
Methods: We used computed tomography (CT) to assess coronary artery calcification score (CACS) using the Agatston method. The TyG index was multiplied by BMI to derive the TyG-BMI index. Ordinal logistic regression models were used to analyze the relationship between TyG-BMI and CAC. The dose-response relationship was evaluated using restricted cubic spline regression. Weighted Quantile Sum regression was used to explore the weight of the TyG-BMI index components.
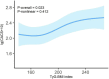
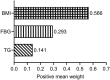
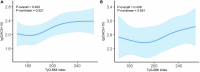
Results: Based on the TyG-BMI, 219 patients with MHD were stratified into three groups. The TyG-BMI index was shown to be an independent risk factor for CACS by multivariate ordinal logistic regression analysis (odds ratio, 1.011; [95% confidence interval, 1.002-1.021]; P = 0.021). The relationship between TyG-BMI and lg (CACS + 10) was linear (P-overall = 0.023, P-non-linear = 0.412). Body mass index (BMI) had the highest weight (0.566) when weights were assigned to the three components of TyG-BMI. In the non-diabetes and diabetes subgroups, TyG-BMI and lg (CACS + 10) did not exhibit a significant non-linear relationship.
Conclusion: TyG-BMI and CAC were independently positively correlated in patients undergoing MHD. These findings suggest that assessing TyG-BMI as a valuable tool for identifying the risk of CAC in patients with MHD.
Keywords: cardiovascular disease; coronary artery calcification; insulin resistance; maintenance hemodialysis; triglyceride glucose-body mass index.
Copyright © 2024 Jiang, Zhu, Ding, Yan, Chen, Wang, Li and Liu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

