The effect of activities of daily living on anxiety in older adult people: the mediating role of social participation
- PMID: 39735764
- PMCID: PMC11671491
- DOI: 10.3389/fpubh.2024.1450826
The effect of activities of daily living on anxiety in older adult people: the mediating role of social participation
Abstract
Objective: Anxiety is a serious psychiatric illness in older adult people. Activities of daily living and social participation are important factors influencing anxiety in older adult people. Using social participation as a mediating variable, this study explored the influence of activities of daily living on anxiety in older adult people to provide scientific evidence for improving the psychological health of older adult people.
Methods: A multistage stratified random sampling method was used in this study to recruit older adult people. T tests and variance analysis were used for single factor analysis, and a multiple linear regression model was used for multifactor analysis. Pearson correlation analysis was used to study the correlation between activities of daily living and social participation and anxiety. The Process program was used to perform the bootstrap test.
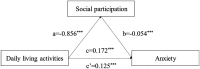
Results: The mean anxiety score of the interviewed older adult individuals was 3.028 ± 4.606 points, and 28.66% of the older adult individuals had anxiety. There was a statistically significant difference in the anxiety scores of older adult people across sex, age, marital status, education level, and health insurance status (p < 0.05). After controlling for other variables, each one-point increase in the activities of daily living score significantly increased the anxiety score by 0.122 points (𝛽=0.122, p < 0.001), and each one-point increase in the social participation score significantly decreased the anxiety score by 0.058 points (𝛽= - 0.058, p < 0.001). According to the results of the mediating effect analysis, there was a significant positive relationship between activities of daily living and anxiety, and the total effect was established (𝛽=0.1719, p < 0.001). After controlling for social participation, there was a significant direct effect of activities of daily living on anxiety in older adult people (𝛽=0.1255, p < 0.001). A partial mediating effect of social participation on the relationship between activities of daily living and anxiety in older adult people was found. The indirect effect of social participation was 26.99%.
Conclusion: Activities of daily living and social participation are important factors affecting anxiety in older adult people. Health education should be increased to enhance the physical activity of older adult people to improve their activities of daily living, create a good atmosphere for their social participation, improve their motivation for and continuity of social participation.
Keywords: activities of daily living; anxiety; mediating effect; older adults; social participation.
Copyright © 2024 Zheng, Xu and Liu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Relationship between social participation and depressive symptoms in patients with multimorbidity: the chained mediating role of cognitive function and activities of daily living.BMC Public Health. 2024 Jul 10;24(1):1844. doi: 10.1186/s12889-024-19157-7. BMC Public Health. 2024. PMID: 38987791 Free PMC article.
-
The impact of social participation on Subjective Wellbeing in the older adult: the mediating role of anxiety and the moderating role of education.Front Public Health. 2024 May 16;12:1362268. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2024.1362268. eCollection 2024. Front Public Health. 2024. PMID: 38818440 Free PMC article.
-
Does internet use promote the health of empty-nest older adults in rural China? The mediating role of social participation using a propensity score matching approach.Front Public Health. 2024 Nov 22;12:1436525. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2024.1436525. eCollection 2024. Front Public Health. 2024. PMID: 39651475 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of environmental modification on activities of daily living, social participation and quality of life in the older adults: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Disabil Rehabil Assist Technol. 2020 Feb;15(2):132-140. doi: 10.1080/17483107.2018.1533595. Epub 2018 Nov 9. Disabil Rehabil Assist Technol. 2020. PMID: 30409070
-
Intrinsic Capacity and Instrumental Activity of Daily Living Among Community Dwelling Elderly in China: The Mediating Effect of Two-Way Social Support and Sense of Coherence.Public Health Nurs. 2025 Mar-Apr;42(2):762-770. doi: 10.1111/phn.13505. Epub 2024 Dec 1. Public Health Nurs. 2025. PMID: 39617636 Review.
Cited by
-
The Impact of Socioeconomic Factors on Cognitive Ability in Community-Dwelling Older Adults: Mediating Effect of Social Participation and Social Support.Healthcare (Basel). 2025 Mar 4;13(5):551. doi: 10.3390/healthcare13050551. Healthcare (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40077112 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Liu Z, Agudamu BT, Bu T, Akpinar S, Jabucanin B. The association between the China's economic development and the passing rate of National Physical Fitness Standards for elderly people aged 60-69 from 2000 to 2020. Front Public Health. (2022) 10:857691. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.857691, PMID: - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization . Mental health of older persons. (2023).Available at: https://www.who.int/en/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/.
-
- Zhao L, Zheng X, Ji K, Wang Z, Sang L, Chen X, et al. . The relationship between social support and anxiety among rural older people in elderly caring social organizations: a cross-sectional study. Int J Environ Res Public Health. (2022) 19:11411. doi: 10.3390/ijerph191811411, PMID: - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical