Intra-neural Ewing Sarcoma of the Radial Nerve Presenting as Wrist
- PMID: 39735801
- PMCID: PMC11676020
- DOI: 10.4103/jwas.jwas_178_23
Intra-neural Ewing Sarcoma of the Radial Nerve Presenting as Wrist
Abstract
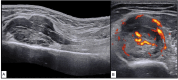
Intra-neural Ewing sarcoma is an extremely rare tumour and only a few isolated case reports exist in the literature. A 32-year-old South Asian male presented with wrist and finger drops of 3 months duration. Further evaluation with ultrasonography and magnetic resonance imaging revealed a tumour of the radial nerve in the arm. A wide excision of the tumour was performed, and the radial nerve was reconstructed with cabled nerve grafts. A diagnosis of extra-osseous Ewing sarcoma (EES) was made after histopathological evaluation using immunohistochemistry techniques. The patient subsequently received chemotherapy and after 5 months, he is disease-free and pain-free. However, there has been no motor recovery yet. Clinical findings and imaging can help and characterise the tumour, but histopathology and analysis for EWSR1 gene rearrangement are essential to confirm the diagnosis. Wide surgical excision and chemotherapy are the mainstay of managing neural EES.
Keywords: Ewing sarcoma; Intra-neural Ewing sarcoma is an extremely rare tumour and only a few isolated case reports exist in the literature; Wide surgical excision and chemotherapy are the mainstays of managing neural extra-osseous Ewing sarcoma; radial nerve; radial nerve palsy.
© 2024 Journal of The West African College of Surgeons.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Mohan AT, Park DH, Jalgaonkar A, Alorjani M, Aston W, Briggs T. Intra-neural Ewing’s sarcoma of the upper limb mimicking a peripheral nerve tumour A report of 2 cases. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2011;64:e153–6. - PubMed
-
- Jamshidi K, Mirzaei A, Bagherifard A, Bahrabadi M. Rare case of small size extraskeletal Ewing sarcoma arising from the median nerve with paresthesia. J Orthop Sci. 2018;23:430–2. - PubMed
-
- Xie CF, Liu MZ, Xi M. Extraskeletal Ewing’s sarcoma: A report of 18 cases and literature review. Chin J Cancer. 2010;29:420–4. - PubMed
-
- Strom T, Kleinschmidt-DeMasters BK, Donson A, Foreman NK, Lillehei KO. Rare nerve lesions of non–nerve sheath origin: A 17-year retrospective series. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2009;133:1391–402. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources