Current and Emerging Techniques for Diagnosis of Toxoplasmosis in Pregnancy: A Narrative Review
- PMID: 39735839
- PMCID: PMC11671817
- DOI: 10.18502/ijpa.v19i4.17159
Current and Emerging Techniques for Diagnosis of Toxoplasmosis in Pregnancy: A Narrative Review
Abstract
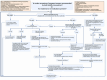
Toxoplasma gondii is an intracellular parasite capable of crossing the placenta in pregnancy and infecting the developing fetus, leading to various congenital anomalies and even abortion. Acute Toxoplasma infection is responsible for almost all cases of congenital toxoplasmosis in immunocompetent pregnant women. Prenatal screening for acute toxoplasmosis primarily involves maternal serology and fetal ultrasound imaging. When serological or ultrasound findings suggest acute infection, further diagnostic tests are necessary to confirm fetal infection. Currently, molecular methods to detect the parasite's DNA, including polymerase chain reaction-based methods, on amniotic fluid are the gold standard tests for the diagnosis of congenital toxoplasmosis. In this review, we aim to discuss various aspects of screening and diagnostic methods for toxoplasmosis in pregnancy, including (i) current serological assays, screening approaches, and future perspectives; (ii) the role of imaging techniques, with an emphasis on ultrasound; (iii) principles and recent advances in diagnostic molecular methods; (iv) emerging techniques, such as point-of-care-based tests and biosensors, and microRNAs as novel biomarkers of acute infection; and (v) an overview of screening programs in different countries, important epidemiological determinants, and recommendations for Toxoplasma screening health policies.
Keywords: Congenital toxoplasmosis; Molecular diagnostics; Pregnancy; Serological assays; Toxoplasma gondii.
© 2024 Teimouri et al. Published by Tehran University of Medical Sciences.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interests The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Toxoplasmosis in pregnancy: prevention, screening, and treatment.J Obstet Gynaecol Can. 2013 Jan;35(1):78-81. doi: 10.1016/s1701-2163(15)31053-7. J Obstet Gynaecol Can. 2013. PMID: 23343802 English, French.
-
Evaluation of serological prenatal screening to detect Toxoplasma gondii infections in Austria.Neonatology. 2013;103(1):27-34. doi: 10.1159/000342625. Epub 2012 Sep 26. Neonatology. 2013. PMID: 23018152
-
Efficacy of amniotic fluid, blood and urine samples for the diagnosis of toxoplasmosis in pregnant women candidates for amniocentesis using serological and molecular techniques.BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2024 Nov 22;24(1):771. doi: 10.1186/s12884-024-06979-x. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2024. PMID: 39578753 Free PMC article.
-
Congenital toxoplasmosis--prenatal aspects of Toxoplasma gondii infection.Reprod Toxicol. 2006 May;21(4):458-72. doi: 10.1016/j.reprotox.2005.10.006. Epub 2005 Nov 28. Reprod Toxicol. 2006. PMID: 16311017 Review.
-
Congenital toxoplasmosis: An overview of the neurological and ocular manifestations.Parasitol Int. 2018 Dec;67(6):715-721. doi: 10.1016/j.parint.2018.07.004. Epub 2018 Jul 21. Parasitol Int. 2018. PMID: 30041005 Review.
Cited by
-
Clinical courses and outcomes of cerebral toxoplasmosis in HIV-positive patients in Shiraz, Southern Iran: a retrospective study.BMC Infect Dis. 2025 Jul 1;25(1):817. doi: 10.1186/s12879-025-11231-8. BMC Infect Dis. 2025. PMID: 40596926 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adem D, Ame M. Toxoplasmosis and its significance in public health: a review. J Biomed Biol Sci. 2023;2(1):1–20.
-
- Márquez-Mauricio A, Caballero-Ortega H, Gómez-Chávez F. Congenital Toxoplasma gondii diagnosis: current approaches and new insights. Acta Parasitol. 2023; 68(3):473–480. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
