Ultrasound as a Diagnostic Modality in Hand and Wrist Musculoskeletal Pathologies: A Narrative Review
- PMID: 39735871
- PMCID: PMC11680561
- DOI: 10.1007/s43465-024-01206-3
Ultrasound as a Diagnostic Modality in Hand and Wrist Musculoskeletal Pathologies: A Narrative Review
Abstract
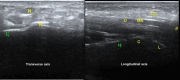
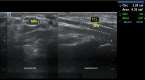
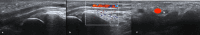
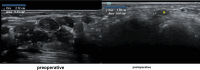
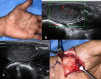
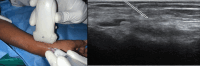
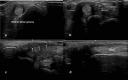
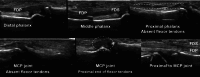
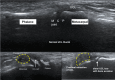
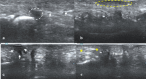
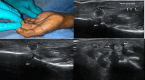
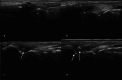
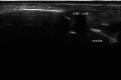
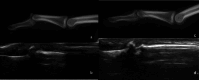
Background: Musculoskeletal ultrasonography of the hand and wrist is becoming the trend in assessing and diagnosing most hand and wrist injuries, soft-tissue mass, and occult fractures. Its advantages include ultra-high frequency probes, noninvasiveness, cost-effectiveness, lack of ionising radiation, and portability. The patients are comfortable doing this procedure in the outpatient department, and visualising the ultrasound images increases their confidence.
Conclusions: Ultrasound has a practical and dynamic real-time diagnostic capability compared to other modalities, playing an important role in hand and wrist pathologies. Apart from the diagnostic utility, it has also been beneficial in musculoskeletal intervention procedures, such as trigger finger, carpal tunnel syndrome, and various tenosynovitis. The learning curve and limited deeper penetrations are relative limitations to ultrasound usage. More dedicated training centres and modules for future generations and CT/MRI for deeper structures are always an alternative. This article reviews the role of ultrasound in hand and wrist pathologies.
Supplementary information: The online version contains supplementary material available at 10.1007/s43465-024-01206-3.
Keywords: Diagnostic modality; Effective; Hand and wrist; Ultrasound.
© Indian Orthopaedics Association 2024. Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interestThe authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures





References
-
- Schuind, F.A., Moungondo, F., & Van Overstraeten, L. (2022). Use of sonography in hand/upper-extremity surgery: innovative concepts and techniques. Hand Clinics,38(1), xiii-xiv. - PubMed
-
- Wong, D. C., Wansaicheong, G. K., & Tsou, I. Y. (2009). Ultrasonography of the hand and wrist. Singapore Medical Journal,50(2), 219–225. PMID: 19296039. - PubMed
-
- Rempel, D., Dahlin, L., & Lundborg, G. (1999). Pathophysiology of nerve compression syndromes: response of peripheral nerves to loading. Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery. American Volume,81(11), 1600–1610. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
