Macrophage Infiltration Correlated with IFI16, EGR1 and MX1 Expression in Renal Tubular Epithelial Cells Within Lupus Nephritis-Associated Tubulointerstitial Injury via Bioinformatics Analysis
- PMID: 39735896
- PMCID: PMC11681807
- DOI: 10.2147/JIR.S489087
Macrophage Infiltration Correlated with IFI16, EGR1 and MX1 Expression in Renal Tubular Epithelial Cells Within Lupus Nephritis-Associated Tubulointerstitial Injury via Bioinformatics Analysis
Abstract
Objective: A comprehensive bioinformatics analysis was conducted to investigate potential new diagnostic biomarkers and immune infiltration characteristics associated with tubulointerstitial injury in lupus nephritis (LN), and to examine possible correlations between key genes and infiltrating immune cells.
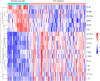
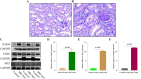
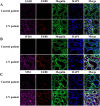
Methods: The GSE32591, GSE113342, and GSE200306 datasets were downloaded from the Gene Expression Omnibus database and differentially expressed genes (DEGs) were identified in the pooled dataset. Support vector machine-recursive feature elimination analysis and the least absolute shrinkage and selection operator regression model were used to screen for possible markers, and the compositional patterns of the 22 types of immune cell fractions in LN were determined using CIBERSORT. Finally, Western blotting, quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction, and multiple immunofluorescence methods were used to confirm the significance of these feature genes in MRL/lpr mice and patients with LN.
Results: Seventeen DEGs were identified, of which 11 were considerably upregulated and six were markedly downregulated. Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes pathway analysis revealed significant enrichment in pertussis, complement and coagulation cascades, systemic lupus erythematosus, and other pathways. Based on the machine learning results, we identified IFI16, EGR1 and MX1 were key diagnostic genes for tubulointerstitial injury associated with LN. Immune cell infiltration analysis revealed that IFI16, EGR1 and MX1 were associated with M1 macrophages. Finally, the association between IFI16, EGR1, MX1 and macrophages in MRL/lpr mice and patients with LN were verified.
Conclusion: This study suggests that IFI16, EGR1 and MX1 which are highly expressed in renal tubular epithelial cells in LN and are associated with macrophage infiltration, may be a novel diagnostic and therapeutic target.
Keywords: EGR1; IFI16; MX1; immune infiltration; lupus nephritis; tubulointerstitial injury.
© 2024 Tian et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declared that they have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures






References
-
- Bajema IM, Wilhelmus S, Alpers CE, et al. Revision of the international society of nephrology/renal pathology society classification for lupus nephritis: clarification of definitions, and modified national institutes of health activity and chronicity indices. Kidney Int. 2018;93(4):789–796. doi:10.1016/j.kint.2017.11.023 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

