Thioredoxin-interacting protein (TXNIP) inhibition promotes retinal ganglion cell survival and facilitates M1-like microglial transformation via the PI3K/Akt pathway in glaucoma
- PMID: 39736512
- PMCID: PMC11687008
- DOI: 10.1186/s10020-024-01058-5
Thioredoxin-interacting protein (TXNIP) inhibition promotes retinal ganglion cell survival and facilitates M1-like microglial transformation via the PI3K/Akt pathway in glaucoma
Abstract
Background: Glaucoma is a group of heterogeneous neurodegenerative diseases with abnormal energy metabolism and imbalanced neuroinflammation in the retina. Thioredoxin-interacting protein (TXNIP) is involved in glucose and lipid metabolism, and associated with oxidative stress and inflammation, however, not known whether to be involved in glaucoma neuropathy and its underlying mechanisms.
Methods: To establish the chronic ocular hypertension (COH) mice model. Western blot, RT-PCR, immunofluorescence and F-VEP were used to detect neuroinflammation level, glial activation and RGCs survival in retina of wild type, TXNIP knockout and MCC950 treatment COH mice. Microglia high-pressure cultured model was constructed. Western blot, RT-PCR and immunofluorescence were used to investigate the proinflammatory cytokines secretion, glucose uptake and phenotype transformation in wild type, TXNIP knockout and overexpressed microglia combined with IL-17A treatment. Finally, we explored the possible underlying mechanisms using relevant pathway inhibitor interventions.
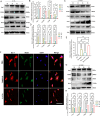
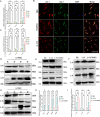
Results: In this study, for the first time we reported that TXNIP expression was remarkably increased in experimental glaucomatous retina of chronic ocular hypertension (COH) mice, and it was mainly expressed in the ganglion cells layer (GCL). In addition, we found that ablation of TXNIP promoted retinal ganglion cells (RGCs) survival and alleviated visual function impairment in experimental glaucoma. Then, we explored the spatiotemporal consistency between glial activation and retinal inflammation levels in COH mice respectively with TXNIP-deficiency and under treatment of a thermo-containing protein domain 3 (NLRP3) inhibitor MCC950, and the results indicated that TXNIP probably mediated neuroinflammation in glaucomatous retina by activating microglia. Furthermore, upregulation of TXNIP was found in pressure-stimulated microglia, whereas silencing TXNIP facilitated microglial polarization trending towards M1 type and reduced glucose transporter-1 (Glut-1) expression on microglia under high pressure in vitro. Moreover, IL-17A was found to play a role in acting synergistically with TXNIP upon the regulation of microglia polarity transformation. Finally, knockout of TXNIP was revealed to promote PI3K phosphorylation, whereas inhibition of PI3K by LY294002 effectively suppressed Glut-1 expression, glucose uptake, and M1-like transformation tendency in microglia obtained from TXNIP-deficiency mice under high pressure stimulation.
Conclusions: TXNIP is significantly involved in the inflammation-related neuropathy of experimental glaucoma and probably facilitates M1-like microglial transformation via PI3K/Akt pathway.
Keywords: Energy metabolism; Experimental glaucoma; Microglia; Neuroinflammation; PI3K/AKT; TXNIP.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: The Animal Care and Use Committee of Ruijin Hospital, Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine approved all animal experimental protocols. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Interleukin-17A modulates retinal inflammation by regulating microglial activation via the p38 MAPK pathway in experimental glaucoma neuropathy.FASEB J. 2023 Jun;37(6):e22945. doi: 10.1096/fj.202202056RR. FASEB J. 2023. PMID: 37144630
-
TXNIP, a novel key factor to cause Schwann cell dysfunction in diabetic peripheral neuropathy, under the regulation of PI3K/Akt pathway inhibition-induced DNMT1 and DNMT3a overexpression.Cell Death Dis. 2021 Jun 23;12(7):642. doi: 10.1038/s41419-021-03930-2. Cell Death Dis. 2021. PMID: 34162834 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of P2X7R- NLRP3 pathway in Retinal microglia contribute to Retinal Ganglion Cells death in chronic ocular hypertension (COH).Exp Eye Res. 2019 Nov;188:107771. doi: 10.1016/j.exer.2019.107771. Epub 2019 Aug 22. Exp Eye Res. 2019. PMID: 31445901
-
Targeting mitochondrial dysfunction: Innovative strategies to combat glaucoma neuroinflammation.Exp Eye Res. 2025 Aug;257:110441. doi: 10.1016/j.exer.2025.110441. Epub 2025 May 21. Exp Eye Res. 2025. PMID: 40409355 Review.
-
Role of Microglia in Glaucomatous Pathology.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2025;1468:149-153. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-76550-6_25. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2025. PMID: 39930188 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Inhibition of the Foxo3/Txnip Axis Alleviates Ventilator-Induced Diaphragmatic Dysfunction by Downregulating MuRF1.Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2025 Aug;197(8):4949-4968. doi: 10.1007/s12010-025-05261-w. Epub 2025 May 16. Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2025. PMID: 40377847
-
PRMT5 Regulates Senescence in Retinal Ganglion Cells by Targeting the Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling Cascade.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2025 Jun 2;66(6):8. doi: 10.1167/iovs.66.6.8. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2025. PMID: 40459496 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Agarwal R, Agarwal P. Rodent models of glaucoma and their applicability for drug discovery. Expert Opin Drug Discov. 2017;12(3):261–70. - PubMed
-
- Ao H, Li H, Zhao X, Liu B, Lu L. TXNIP positively regulates the autophagy and apoptosis in the rat müller cell of diabetic retinopathy. Life Sci. 2021;267: 118988. - PubMed
-
- Baudouin C, Kolko M, Melik-Parsadaniantz S, Messmer EM. Inflammation in glaucoma: from the back to the front of the eye, and beyond. Prog Retin Eye Res. 2021;83: 100916. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 82371048/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 82070953/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 82000885/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 21Y11909700/Science and Technology Innovation Plan Of Shanghai Science and Technology Commission
- 202140130/Shanghai Municipal Health Commission
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

