Androgen deprivation therapy use and the risk of heart failure in patients with prostate cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 39736562
- PMCID: PMC11684147
- DOI: 10.1186/s12872-024-04421-w
Androgen deprivation therapy use and the risk of heart failure in patients with prostate cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Background & aim: We aimed in this study to investigate the relationship between Androgen Deprivation Therapy (ADT) use and the risk of heart failure in patients with prostate cancer. In this research, the negative or positive effects of ADT in the development of cardiovascular diseases or its exacerbation in people with prostate cancer have been investigated.
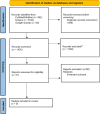
Materials and methods: For this research, we reviewed articles from PubMed, Scopus, and Google Scholar databases until February 2024. We extracted and screened titles, abstracts, and full texts of related articles. The quality of studies was assessed and extracted and analyzed data.
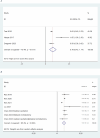
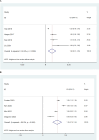
Result: A total of 9 studies comprising 189,045 patients were included in the meta-analysis, examining the association between androgen deprivation therapy (ADT) and heart failure. The overall pooled hazard ratio (HR) was 1.299 (95% CI: 1.003-1.595), indicating a significantly increased risk of heart failure with ADT. Subgroup analyses revealed that the risk was stronger in Asian populations (pooled HR = 1.545, 95% CI: 1.180-1.910) compared to North American populations (pooled HR = 0.779, 95% CI: 0.421-1.138).
Conclusions: ADT has a significant relationship with cardiovascular disease. According to the analysis, ADT has increased the risk of heart failure in people with prostate cancer by 30%.
Keywords: Androgen deprivation therapy; Cardiovascular disease; Prostate cancer; heart failure.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

