A rapid visual detection method for porcine teschovirus through reverse transcription recombinase-aided amplification coupled with lateral flow dipstick
- PMID: 39736581
- PMCID: PMC11687080
- DOI: 10.1186/s12917-024-04442-9
A rapid visual detection method for porcine teschovirus through reverse transcription recombinase-aided amplification coupled with lateral flow dipstick
Abstract
Background: Porcine teschovirus (PTV) is an important enteropathogen, associated with symptoms of polioencephalomyelitis, pneumonia, pericarditis, myocarditis, diarrhea, and reproductive disorders in pigs. Rapid and precise diagnostic methods are essential for managing PTV infections. The study introduced a simple, quick, and visual approach for detecting PTV through the use of RT-RAA coupled with LFD.
Results: The procedures of RT-RAA-LFD for PTV could be carried out with 1.0 μmol/L primer concentration and 2.0 μmol/L probe concentration at 37 °C for 20 min, and the amplification result could be visualized within 5 min through LFD detection. Meanwhile, the assay established in this study showed no interaction with other associated diarrhea viruses, and has high specificity to PTV, with a minimal detection limit of 10 copies/μL and good repeatability. 128 clinical samples suspected of having a PTV infection were tested by RT-PCR and RT-RAA-LFD, respectively. The total diagnostic coincidence rate was 98.44% (126/128) with a Kappa value of 0.96(K ≥ 0.75), demonstrating a high degree of agreement to detect PTV for the two methods.
Conclusions: The RT-RAA-LFD assay created in this research displayed quick response, specificity, and sensitivity, capable of successfully detecting PTV in less than 25 min, providing an easy-to-use diagnostic instrument for rapid and visual PTV detection, especially suitable for labs and low-resource environments.
Keywords: Lateral flow dipstick; Porcine teschovirus; Recombinase-aided amplification; Visual detection method.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: The Administration of Affairs Concerning Experimental Animals' rules, as well as the Institute of Animal Husbandry and Veterinary Medicine's (FAAS) Laboratory Animal Bioethics Committee's approval of animal ethics guidelines and protocol, were followed in the sampling and handling of the samples. The ethics committee's permission numbers were IAHV-AEC-2022–089. The farm owner got our written notification and consented to the collection of samples. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


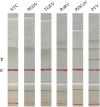

References
-
- Dunne HW, Gobble JL, Hokanson JF, Kradel DC, Bubash GR. Porcine reproductive failure associated with a newly identified “SMEDI” group of picorna viruses. Am J Vet Res. 1965;26(115):1284–97. - PubMed
-
- Matias Ferreyra F, Arruda B, Stevenson G, Schwartz K, Madson D, Yoon KJ, Zhang J, Piñeyro P, Chen Q, Arruda P: Development of Polioencephalomyelitis in Cesarean-Derived Colostrum-Deprived Pigs Following Experimental Inoculation with Either Teschovirus A Serotype 2 or Serotype 11. Viruses 2017, 9(7). - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

