Activity of CDK4/6 inhibitors and parameters affecting survival in elderly patients in age-subgroups: Turkish Oncology Group (TOG) retrospective study
- PMID: 39736618
- PMCID: PMC11687141
- DOI: 10.1186/s12885-024-13357-5
Activity of CDK4/6 inhibitors and parameters affecting survival in elderly patients in age-subgroups: Turkish Oncology Group (TOG) retrospective study
Abstract
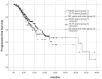
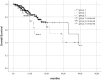
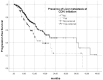
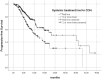
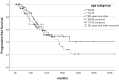
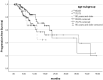
Highly selective inhibitors of cyclin-dependent kinase 4 and 6 (CDK4/6is) have emerged as a standart of care for first- and second-line therapies in combination with endocrine therapy (ET) for HR+/HER2- metastatic breast cancer (MBC) patients. It has been reported that combination therapy is more effective than ET alone and is safe in elderly patients as well as young patients. Nevertheless, elderly and very old patients with HR+/HER2-MBC treated with CDK4/6 inhibitor (CDK4/6i) combinations are relatively underrepresented in randomized controlled trials. To contribute to the literature, we investigated the real-world efficacy, factors associated with survival and the rates of adverse events (AEs) of the treatment with palbociclib or ribociclib plus ET in the HR+/HER2- MBC patient cohort over the age of 65 for age subgroups. In this retrospective study, 348 patients were divided into subgroups: 65-69 years old, 70-79 years old and 80 years and older. Median PFS (mPFS) for whole group was 18.3 (95% CI,14.3-22.3) months. There was no significant difference in mPFS between age groups (p = 0.75). The estimated median OS (mOS) was 39.5 (95% CI, 24.9-54.1) months and there was no significant difference between age groups (p = 0.15). There was a meaningfull numerical difference that did not reach statistical significance in patients who received CDK4/6i treatment as the first line for MBC. Grade 3-4 AEs were reported in 42.7% for the entire group, and neutropenia was the most common (37.3%). It can be concluded that combination therapy with palbociclib or ribociclib with an ET partner has similar efficacy and is safe among subgroups of older patients diagnosed with HR+/HER2-MBC.
Keywords: CDK 4/6 inhibitors; Geriatric population; Metastatic breast cancer.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: The study protocol was approved by the Clinical Research Ethics Committee chaired by the Ankara City Hospital Institutional Review Board. Informed consent was waived by our institutional review board because no experimental procedures were performed. The preparation of the article was followed in accordance with the STROBE guidelines. We conducted this study according to the Declaration of Helsinki. Consent for publication: Not Applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Clinical benefit and safety profile of cross-line therapy with CDK4/6 inhibitors: a retrospective study of HR+/HER2- advanced breast cancer.Cancer Biol Med. 2024 Sep 11;21(10):934-50. doi: 10.20892/j.issn.2095-3941.2024.0204. Cancer Biol Med. 2024. PMID: 39267478 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative overall survival of CDK4/6 inhibitors plus an aromatase inhibitor in HR+/HER2- metastatic breast cancer in the US real-world setting.ESMO Open. 2025 Jan;10(1):104103. doi: 10.1016/j.esmoop.2024.104103. Epub 2025 Jan 3. ESMO Open. 2025. PMID: 39754979 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy of first-line CDK 4-6 inhibitors in premenopausal patients with metastatic breast cancer and the effect of dose reduction due to treatment-related neutropenia on efficacy: a Turkish Oncology Group (TOG) study.J Chemother. 2025 Feb;37(1):69-75. doi: 10.1080/1120009X.2024.2330835. Epub 2024 Mar 18. J Chemother. 2025. PMID: 38497444
-
CDK4/6 Inhibitors Expand the Therapeutic Options in Breast Cancer: Palbociclib, Ribociclib and Abemaciclib.BioDrugs. 2019 Apr;33(2):125-135. doi: 10.1007/s40259-019-00337-6. BioDrugs. 2019. PMID: 30847853 Review.
-
QTc prolongation across CDK4/6 inhibitors: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.JNCI Cancer Spectr. 2024 Sep 2;8(5):pkae078. doi: 10.1093/jncics/pkae078. JNCI Cancer Spectr. 2024. PMID: 39254653 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Updated efficacy and safety of CDK4/6 inhibitors plus endocrine therapy in elderly women with HR+/HER-2 metastatic or advanced breast cancer: patient-level network meta-analysis.Aging (Albany NY). 2025 May 25;17(5):1313-1327. doi: 10.18632/aging.206257. Epub 2025 May 25. Aging (Albany NY). 2025. PMID: 40440494 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rugo HS, et al. Effect of palbociclib plus endocrine therapy on time to chemotherapy across subgroups of patients with hormone receptor–positive/human epidermal growth factor receptor 2–negative advanced breast cancer: Post hoc analyses from PALOMA-2 and PALOMA-3. Breast. 2022;66:324–31. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Hortobagyi GN, et al. Ribociclib as First-Line therapy for HR-Positive, advanced breast Cancer. N Engl J Med. 2016;375(18):1738–48. - PubMed
-
- Goetz MP, et al. MONARCH 3: Abemaciclib as initial therapy for advanced breast Cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2017;35(32):3638–46. - PubMed
-
- Giuliano M, et al. Endocrine treatment versus chemotherapy in postmenopausal women with hormone receptor-positive, HER2-negative, metastatic breast cancer: a systematic review and network meta-analysis. Lancet Oncol. 2019;20(10):1360–9. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

