The effect of online training based on stroke educational program on patient's quality of life and caregiver's care burden: a randomized controlled trial
- PMID: 39736718
- PMCID: PMC11686964
- DOI: 10.1186/s12912-024-02629-x
The effect of online training based on stroke educational program on patient's quality of life and caregiver's care burden: a randomized controlled trial
Abstract
Background: Stroke is considered one of the leading causes of both mortality and morbidity on a global scale. The significant impact on the health and quality of life of stroke survivors and their caregivers is well-acknowledged due to the stressful consequences of dependency and the need for home care. This study aims to examine the impact of online training utilizing a stroke educational program on the patient's quality of life and their caregivers' care burden.
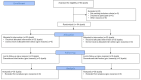
Materials and methods: From March to August 2024, a randomized, controlled trial was conducted. In this study, a total of 60 dyads consisting of stroke patients and their caregivers participated. Participants were selected by convenient sampling method and then randomly allocated into intervention and control groups using research randomizer software. The participants in the intervention group received the educational content through the WhatsApp application during a series of fifteen sessions, each lasting between 45 and 60 min. The control group was given standard hospital education. The data collection and analysis process entailed the utilization of questionnaires, which encompassed demographics, the Stroke Specific Quality of Life Scale (SS-QOL), and the Zarit burden of care questionnaires.
Results: In the intervention group, the average age of patients and caregivers was 60.23 ± 12.41 and 51.56 ± 10.42, respectively, while in the control group, it was 61.73 ± 12.61 and 53.60 ± 9.03, respectively. The intervention group demonstrated a statistically significant difference in the mean score of patient's quality of life, comparing the baseline with the post-intervention periods (134.73 ± 33.51 vs. 90.56 ± 6.51 and 130.46 ± 30.67 vs. 90.56 ± 6.51; p < 0.05). Furthermore, a statistically significant difference in the mean score of caregiver's care burden was noted between the baseline and post-intervention periods (80.23 ± 7.99 vs. 65.43 ± 16.52 and 80.23 ± 7.99 vs. 60.53 ± 21.34; p < 0.05).
Conclusion: The implementation of an online training program focused on stroke education, resulted in an improvement in the quality of life for stroke patients, as well as a reduction in the care burden for their caregivers. As a result, it is essential to provide education to patients and their caregivers to improve patient care and minimize stroke complications.
Trial registration: IRCT20240609062065N1, 2024/08/31.
Keywords: Caregiver burden; Educational program; Quality of life; Stroke.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Participants in the study were provided with information about the purpose of the study and the assurances were given to them regarding the protection of their privacy and confidentiality. They were informed that the study is optional, and they possess the freedom to discontinue their involvement whenever they choose. Before participating in the study, they signed a consent form. Additionally, Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences’ Review Board approved the study. This study was approved by the Research Committee of Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences (No: IR.SBMU.PHARMACY.REC.1402.178). Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests. Protocol registration: The study protocol was registered in the Iranian Registry of Clinical Trials (No: IRCT20240609062065N1, 2024/08/31).
Figures
References
-
- Tsivgoulis G, Patousi A, Pikilidou M, Birbilis T, Katsanos AH, Mantatzis M, et al. Stroke incidence and outcomes in northeastern Greece: the Evros Stroke Registry. Stroke. 2018;49(2):288–95. - PubMed
-
- Katan M, Luft A, editors. Global burden of stroke 2018: Thieme Medical. - PubMed
-
- Mendis S. Stroke disability and rehabilitation of stroke: World Health Organization perspective. Int J stroke. 2013;8(1):3–4. - PubMed
-
- Kable A, Pond D, Baker A, Turner A, Levi C. Evaluation of discharge documentation after hospitalization for stroke patients discharged home in Australia: a cross-sectional, pilot study. Nurs Health Sci. 2018;20(1):24–30. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials