A chitosan/acellular matrix-based neural graft carrying mesenchymal stem cells to promote peripheral nerve repair
- PMID: 39736729
- PMCID: PMC11687163
- DOI: 10.1186/s13287-024-04093-5
A chitosan/acellular matrix-based neural graft carrying mesenchymal stem cells to promote peripheral nerve repair
Abstract
Background: Treatment of peripheral nerve defects is a major concern in regenerative medicine. This study therefore aimed to explore the efficacy of a neural graft constructed using adipose mesenchymal stem cells (ADSC), acellular microtissues (MTs), and chitosan in the treatment of peripheral nerve defects.
Methods: Stem cell therapy with acellular MTs provided a suitable microenvironment for axonal regeneration, and compensated for the lack of repair cells in the neural ducts of male 8-week-old Sprague Dawley rats.
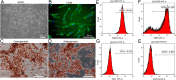
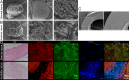
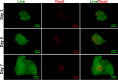
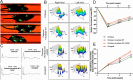
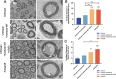
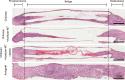
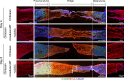
Results: In vitro, acellular MTs retained the intrinsic extracellular matrix and improved the narrow microstructure of acellular nerves, thereby enhancing cell functionality. In vivo neuroelectrophysiological studies, gait analysis, and sciatic nerve histology demonstrated the regenerative effects of active acellular MT. The Chitosan + Acellular-MT + ADSC group exhibited superior myelin sheath quality and improved neurological and motor function recovery.
Conclusions: Active acellular-MTs precellularized with ADSC hold promise as a safe and effective clinical treatment method for peripheral nerve defects.
Keywords: Acellular nerve; Biomaterials; Chitosan; Mesenchymal stem cells; Peripheral nerve injury; Tissue repair.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Title of the approved project: Nerve defect animal model(SD rats). Name of the institutional approval committee: the Ethics Committee of the Chinese PLA General Hospital. Approval number: SQ2022437. Date of approval: 2022-04-03. (2)Title of the approved project: Preparation of acellular nerves(SD rats). Name of the institutional approval committee: the Ethics Committee of the Chinese PLA General Hospital. Approval number:2022-X18-37. Date of approval:2022-01-08. In this study, all animal experiments were carried out following the guidelines and regulations related to the care and use of laboratory animals presented by the animal ethics committee of the Chinese PLA General Hospital (Code No.2022-X18-37). Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Recellularized nerve allografts with differentiated mesenchymal stem cells promote peripheral nerve regeneration.Neurosci Lett. 2012 Apr 11;514(1):96-101. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2012.02.066. Epub 2012 Mar 3. Neurosci Lett. 2012. PMID: 22405891
-
Transplantation of adipose-derived stem cells for peripheral nerve repair.Int J Mol Med. 2011 Oct;28(4):565-72. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2011.725. Epub 2011 Jun 17. Int J Mol Med. 2011. PMID: 21687931
-
Schwann cells and mesenchymal stem cells in laminin- or fibronectin-aligned matrices and regeneration across a critical size defect of 15 mm in the rat sciatic nerve.J Neurosurg Spine. 2018 Jan;28(1):109-118. doi: 10.3171/2017.5.SPINE161100. Epub 2017 Nov 10. J Neurosurg Spine. 2018. PMID: 29125428
-
Adipose tissue stem cells in peripheral nerve regeneration-In vitro and in vivo.J Neurosci Res. 2021 Feb;99(2):545-560. doi: 10.1002/jnr.24738. Epub 2020 Oct 18. J Neurosci Res. 2021. PMID: 33070351 Review.
-
Mesenchymal Stem Cell Treatment for Peripheral Nerve Injuries.J Cell Physiol. 2025 Apr;240(4):e70031. doi: 10.1002/jcp.70031. J Cell Physiol. 2025. PMID: 40211799 Review.
Cited by
-
Mesenchymal stem cell-based therapy for peripheral nerve injuries: A promise or reality?World J Stem Cells. 2025 Jun 26;17(6):107833. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v17.i6.107833. World J Stem Cells. 2025. PMID: 40585952 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Overcoming acquired immunotherapy resistance in non-small cell lung cancer using ginsenoside Rb1-loaded, peptide-enhanced exosome delivery systems.J Nanobiotechnology. 2025 Jun 13;23(1):443. doi: 10.1186/s12951-025-03456-1. J Nanobiotechnology. 2025. PMID: 40514658 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

