The multifaceted roles of cathepsins in immune and inflammatory responses: implications for cancer therapy, autoimmune diseases, and infectious diseases
- PMID: 39736788
- PMCID: PMC11687005
- DOI: 10.1186/s40364-024-00711-9
The multifaceted roles of cathepsins in immune and inflammatory responses: implications for cancer therapy, autoimmune diseases, and infectious diseases
Abstract
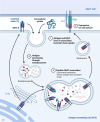
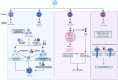
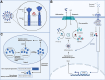
The cathepsin family comprises lysosomal proteases that play essential roles in various physiological processes, including protein degradation, antigen presentation, apoptosis, and tissue remodeling. Dysregulation of cathepsin activity has been linked to a variety of pathological conditions, such as cancer, autoimmune diseases, and neurodegenerative disorders. Understanding the functions of cathepsins is crucial for gaining insights into their roles in both health and disease, as well as for developing targeted therapeutic approaches. Emerging research underscores the significant involvement of cathepsins in immune cells, particularly T cells, macrophages, dendritic cells, and neutrophils, as well as their contribution to immune-related diseases. In this review, we systematically examine the impact of cathepsins on the immune system and their mechanistic roles in cancer, infectious diseases, autoimmune and neurodegenerative disorders, with the goal of identifying novel therapeutic strategies for these conditions.
Keywords: Autoimmune diseases; Cancer therapy; Cathepsins in immune cells; Infectious diseases.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Not applicable. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

