Taltirelin induces TH expression by regulating TRHR and RARα in medium spiny neurons
- PMID: 39736794
- PMCID: PMC11687129
- DOI: 10.1186/s12967-024-06020-x
Taltirelin induces TH expression by regulating TRHR and RARα in medium spiny neurons
Abstract
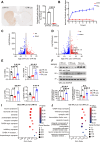
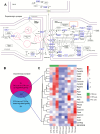
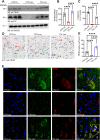
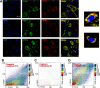
Taltirelin, an orally effective thyrotropin-releasing hormone analog, significantly improves motor impairments in rat models of Parkinson's disease (PD) and enhances dopamine release within the striatum. However, the underlying mechanism remains unclear. In this study, a variety of in vivo and in vitro methods, including transcriptomic analysis, were employed to elucidate the effects of Taltirelin on cellular composition and signaling pathways in the striatum of hemi-PD rats. We demonstrated that Taltirelin upregulates the expression of TRHR on striatal GABAergic neurons, which is accompanied by activation of the TRHR-MAPK-RARα-DRD2 pathway. Consequently, Taltirelin induces medium spiny neurons in the striatum to express TH. This discovery provides valuable insights into the potential application of Taltirelin in neurological disorders and offers new directions for drug development.
Keywords: Dopamine receptor D2; Taltirelin; Thyrotropin-releasing hormone receptor; Tyrosine hydroxylase.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures




References
-
- Kelly JA, Boyle NT, Cole N, Slator GR, Colivicchi MA, Stefanini C, et al. First-in-class thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH)-based compound binds to a pharmacologically distinct TRH receptor subtype in human brain and is effective in neurodegenerative models. Neuropharmacology. 2015;89:193–203. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

