Functional screening identifies miRNAs with a novel function inhibiting vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation
- PMID: 39736815
- PMCID: PMC11852670
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2024.12.037
Functional screening identifies miRNAs with a novel function inhibiting vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation
Abstract
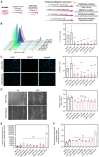
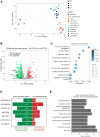
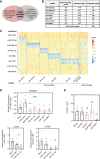
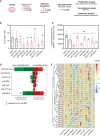
Proliferation of vascular smooth muscle cells (vSMCs) is a crucial contributor to pathological vascular remodeling. MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are powerful gene regulators and attractive therapeutic agents. Here, we aimed to systematically identify and characterize miRNAs with therapeutic potential in targeting vSMC proliferation. Using high-throughput screening, we assessed the impact of 2,042 human miRNA mimics on vSMC proliferation and identified seven miRNAs with novel vSMC anti-proliferative function: miR-323a-3p, miR-449b-5p, miR-491-3p, miR-892b, miR-1827, miR-4774-3p, and miR-5681b. miRNA-mimic treatment affects proliferation of vSMCs from different vascular beds. Focusing on vein graft failure, where miRNA-based therapeutics can be applied to the graft ex vivo, we showed that these miRNAs reduced human saphenous vein smooth muscle cell (HSVSMC) proliferation without toxic effect. HSVSMC transcriptomics revealed a distinct set of targets for each miRNA, leading to the common downregulation of a cell-cycle gene network for all miRNAs. For miR-449b-5p, we showed that its candidate target, CCND1, contributes to HSVSMC proliferation. In contrast to HSVSMCs, miRNA overexpression in endothelial cells led to a limited response in terms of proliferation and transcriptomics. In an ex vivo vein organ model, overexpression of miR-323a-3p and miR-449b-5p reduced medial proliferation. Collectively, the results of our study show the therapeutic potential of seven miRNAs to target pathological vascular remodeling.
Keywords: miRNA therapeutics; microRNA; migration; proliferation; vascular smooth muscle cell; vein graft failure.
Copyright © 2025 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare the following financial interests/personal relationships that may be considered potential competing interests: A.H.B., M.G., and S.Z. are named inventors on a patent application related to this work (PCT/GB2023/052170).
Figures


References
-
- Bacakova L., Travnickova M., Filova E., Matějka R., Stepanovska J., Musilkova J., Zarubova J., Molitor M. In: Muscle Cell and Tissue. Sakuma K., editor. InTech; 2018. The role of vascular smooth muscle cells in the physiology and pathophysiology of blood vessels; pp. 229–257. - DOI
-
- Wang D., Uhrin P., Mocan A., Waltenberger B., Breuss J.M., Tewari D., Mihaly-Bison J., Huminiecki Ł., Starzyński R.R., Tzvetkov N.T., et al. Vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation as a therapeutic target. Part 1: molecular targets and pathways. Biotechnol. Adv. 2018;36:1586–1607. doi: 10.1016/j.biotechadv.2018.04.006. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

