MiR-192-5p targets cell cycle regulation in diabetic kidney disease via cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 3
- PMID: 39736853
- PMCID: PMC11683246
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ncrna.2024.11.003
MiR-192-5p targets cell cycle regulation in diabetic kidney disease via cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 3
Abstract
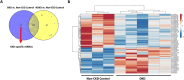
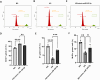
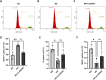
Diabetic kidney disease (DKD), a.k.a diabetic nephropathy, is a leading cause of end-stage renal disease. However, in a fair percentage of patients with type-2 diabetes, renal involvement also occurs due to non-diabetic reasons (non-diabetic kidney disease, NDKD). In this study, we identified miRNA-mRNA regulatory networks specific to human DKD pathogenesis. miRNA profiling of the renal biopsy from cases (DKD, n = 5), disease controls (T2DM with NDKD, n = 6), and non-diabetic, non-CKD controls (patients undergoing nephrectomy for renal cancer, n = 3) revealed 68 DKD-specific miRNA regulation. Sixteen target mRNAs of these DKD-miRNAs were found to have a negative association with the estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) in patients with DKD. The renal gene expression and eGFR data of DKD patients (n = 10-18) in the NephroSeq database were used. Based on these findings, 11 miRNA-mRNA regulatory networks were constructed for human DKD pathogenesis. Of these, in-vitro validation of miR-192-5p- CDKN3 (Cell cycle-dependent kinase inhibitor 3) network was done as miR-192-5p exhibited a maximum number of target genes in the identified DKD regulatory networks, and CDKN3 appeared as a novel target of miR-192-5p in our study. We demonstrated that miR-192-5p overexpression or knockdown of CDKN3 attenuated high glucose-induced apoptosis, fibrotic gene expression, cell hypertrophy, and cell cycle dysregulation and improved viability of proximal tubular cells. Moreover, miR-192-5p overexpression significantly inhibited CDKN3 mRNA and protein expression in proximal tubular cells. Overall, 11 miRNA-mRNA regulatory networks were predicted for human DKD pathogenesis; among these, the association of miR-192-5p- CDKN3 network DKD pathogenesis was confirmed in proximal tubular cell culture.
Keywords: Cell cycle-dependent kinase inhibitor; Diabetic kidney disease; Diabetic nephropathy; High glucose; miRNA-mRNA regulatory networks.
© 2024 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures







References
-
- Erdogmus S., Kiremitci S., Celebi Z.K., Akturk S., Duman N., Ates K., Erturk S., Nergizoglu G., Kutlay S., Sengul S., Ensari A., Keven K. Non-diabetic kidney disease in type 2 diabetic patients: prevalence, clinical predictors and outcomes. Kidney Blood Press. Res. 2017;42:886–893. doi: 10.1159/000484538. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

