Hematological and thermographical changes in rat's model exposed to long-term RF modulated signals
- PMID: 39737009
- PMCID: PMC11682759
- DOI: 10.5455/OVJ.2024.v14.i11.12
Hematological and thermographical changes in rat's model exposed to long-term RF modulated signals
Abstract
Background: Long-term exposure to LTE signals at different frequencies has become a crucial problem in our daily life.
Aim: The aim of the study to figure out the thermal influence of LTE signals (850 MHz, 1800 MHz, and 2600 MHz) on hematological values in rat's model during different periods.
Methods: Forty adult male rats were randomly distributed into four equal groups (control, 850 MHz, 1800 MHz, and 2600 MHz exposure groups). The rats were exposed for 2 hours per day over a period of up to 60 days using a radiofrequency generator.
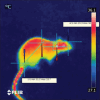
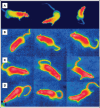
Results: The results showed that the different frequencies have different effects on both hematological and thermo-graphical image analysis.
Conclusion: The study findings demonstrate that these LTE frequencies have a detrimental effect on the rat model through thermal mechanisms.
Keywords: Hematological; LTE signals; Thermographic changes.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors had no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Abduch, N.G., Pires, B.V., Souza, L.L., Vicentini, R.R., Zadra, L.E.F., Fragomeni, B.O., Silva, R.M.O., Baldi, F., Paz, C.C.P. and Stafuzza, N.B. 2022. Effect of thermal stress on +thermoregulation, hematological and hormonal characteristics of caracu beef cattle. Animals (Basel). 12(24), 3473. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Al Abas, M.A.A. and AL-Hakkak, Z.M.M. 2021. Effect exposure of mobile phone radiation on blood parameters in rats. Iraqi J. Sci. 62(11), 4225–4231.
-
- Alchalabi, A.S., Asim, R., Rahim, H. and Abdul Malek, M.F. 2021. Evaluation of the thermal effect of LTE 2600 MHz (4G) electromagnetic field (EMF) exposure: thermographic study on rats. Iraqi J. Vet. Sci. 35(2), 279–285.
-
- Asl, J.F., Goudarzi, M. and Shoghi, H. 2020. The radio-protective effect of rosmarinic acid against mobile phone and Wi-Fi radiation-induced oxidative stress in the brains of rats. Pharmacol. Rep. 72, 857–866. - PubMed
-
- Cao, Y., Li, S. and Chen, J. 2021. Modeling better in vitro models for the prediction of nanoparticle toxicity: a review. Toxicol. Mech. Methods. 31(1), 1–17. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
