Temporary circular external fixation for effective management of bilateral radial non-union in a Toy Poodle
- PMID: 39737051
- PMCID: PMC11682741
- DOI: 10.5455/OVJ.2024.v14.i11.43
Temporary circular external fixation for effective management of bilateral radial non-union in a Toy Poodle
Abstract
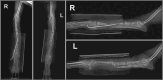
Background: Distal radius fractures are prevalent in small and toy-breed dogs, presenting significant treatment challenges due to complications such as delayed union or non-union. These complications are often exacerbated by reduced vascular density at the distal diaphyseal-metaphyseal junction of the radius, which is vital for bone healing, particularly in toy and small breed dogs. Circular external fixation (CEF) is known for its effectiveness in managing acute and chronic fractures and providing temporary stabilization in humans. This study documented the use of temporary CEF in a Toy Poodle with non-union fractures of the radius and ulna, addressing bone atrophy and resorption caused by repeated implant failures.
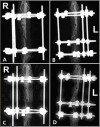
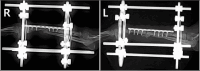
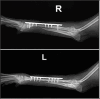
Case description: A 3-year-old, 4.2 kg, neutered male Toy Poodle was referred for treatment after multiple attempts to fix radial and ulnar fractures failed to achieve union over 1 year, leaving the dog barely using its forelimbs. In the first surgery, CEF was applied to heal holes in the bone caused by previous fixation devices and encourage forelimb use through rehabilitation. In the second surgery, a combination of cancellous bone grafting, plate fixation, and CEF was used, resulting in successful bone union and restoration of normal gait after 10 weeks.
Conclusion: In conclusion, CEF is a valuable option for temporary fixation and fracture reduction in toy-breed dogs and offers a promising approach to managing challenging cases.
Keywords: Circular external fixation; Fracture; Non-union; Small animal; Toy-breed dog.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Clinical outcomes of 119 miniature- and toy-breed dogs with 140 distal radial and ulnar fractures repaired with free-form multiplanar type II external skeletal fixation.Vet Surg. 2019 Aug;48(6):938-946. doi: 10.1111/vsu.13245. Epub 2019 May 29. Vet Surg. 2019. PMID: 31140637
-
Radius and ulna fracture repair with the IMEX miniature circular external skeletal fixation system in 37 small and toy breed dogs: A retrospective study.Vet Surg. 2017 May;46(4):587-595. doi: 10.1111/vsu.12647. Epub 2017 Mar 28. Vet Surg. 2017. PMID: 28370231
-
Augmentation of diaphyseal fractures of the radius and ulna in toy breed dogs using a free autogenous omental graft and bone plating.Vet Comp Orthop Traumatol. 2015;28(2):131-9. doi: 10.3415/VCOT-14-02-0020. Epub 2015 Feb 23. Vet Comp Orthop Traumatol. 2015. PMID: 25703613
-
Radius/Ulna fracture repair.Clin Tech Small Anim Pract. 2004 Aug;19(3):128-33. doi: 10.1053/j.ctsap.2004.09.005. Clin Tech Small Anim Pract. 2004. PMID: 15712459 Review.
-
Treatment of open, delayed union, and nonunion fractures with external skeletal fixation.Vet Clin North Am Small Anim Pract. 1992 Jan;22(1):195-207. doi: 10.1016/s0195-5616(92)50014-6. Vet Clin North Am Small Anim Pract. 1992. PMID: 1539427 Review.
References
-
- Aikawa, T., Miyazaki, Y., Shimatsu, T., Iizuka, K. and Nishimura, M. 2018. Clinical outcomes and complications after open reduction and internal fixation utilizing conventional plates in 65 distal radial and ulnar fractures of miniature- and toy-breed dogs. Vet. Comp. Orthop. Traumatol. 31(3), 214–217. - PubMed
-
- Bose, D. and Piper, D. 2021. Temporary external fixation in the management of orthopaedic trauma. Orthop. Trauma. 35(2), 80–83.
-
- Chen, J.C., Carter, D.R. and Williams, L. 2005. Important concepts of mechanical regulation of bone formation and growth. Curr. Opin. Orthop. 16(5), 338–345.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
