The chain mediating role of rumination and psychological resilience in symptom burden and kinesiophobia in patients with chronic heart failure
- PMID: 39737100
- PMCID: PMC11683137
- DOI: 10.3389/fpsyt.2024.1474715
The chain mediating role of rumination and psychological resilience in symptom burden and kinesiophobia in patients with chronic heart failure
Abstract
Objective: To explore the chain-mediating role and impact of rumination and psychological resilience on symptom burden and kinesiophobia in patients with chronic heart failure.
Methods: We selected a total of 318 patients with chronic heart failure from a hospital in Wuxi between November 2023 and May 2024 using a convenience sampling method. Various scales and questionnaires assessed general information, symptom burden, resilience, rumination thinking, and kinesiophobia. Statistical analysis was conducted using SPSS and the bootstrap method to examine the chain mediation effect.
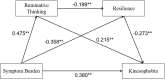
Results: The scores for symptom burden, rumination, psychological resilience, and kinesiophobia in patients with chronic heart failure were 0.81± 0.47, 50.63± 9.02, 23.43± 6.26, and 38.91± 8.01, respectively. Mediation analysis showed that symptom burden had a direct positive predictive effect on rumination (β = 0.475, 95% CI: 0.365-0.584), rumination had a direct negative predictive effect on psychological resilience (β = -0.199, 95% CI: -0.306-0.092), and psychological resilience had a direct negative predictive effect on kinesiophobia (β = -0.273, 95% CI: -0.340-0.206). Rumination and psychological resilience played a chain mediation role between symptom burden and kinesiophobia, with a total effect of 0.606, a direct effect of 0.380, and an indirect effect of 0.226. The mediation effect accounted for 37.29% of the total effect.
Conclusion: Kinesiophobia is at a high level in patients with chronic heart failure. Symptom burden can affect patients' kinesiophobia through the independent or chain mediation effects of rumination and psychological resilience. Healthcare professionals should actively adopt strategies to address symptom burden and rumination while enhancing psychological resilience to reduce patients' kinesiophobia.
Keywords: chain mediation; chronic heart failure; kinesiophobia; resilience; rumination; symptom burden.
Copyright © 2024 Li, Cheng and Jiang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The impact of somatic symptoms on kinesiophobia after esophagectomy among cancer patients: the mediating roles of intrusive rumination and avoidant coping.Support Care Cancer. 2024 Oct 10;32(11):719. doi: 10.1007/s00520-024-08902-8. Support Care Cancer. 2024. PMID: 39387936
-
Relationship between rumination and post-traumatic growth in mobile cabin hospital nurses: The mediating role of psychological resilience.Prev Med Rep. 2023 May 27;34:102266. doi: 10.1016/j.pmedr.2023.102266. eCollection 2023 Aug. Prev Med Rep. 2023. PMID: 37288138 Free PMC article.
-
Mindfulness and negative emotions among Chinese college students: chain mediation effect of rumination and resilience.Front Psychol. 2023 Dec 21;14:1280663. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2023.1280663. eCollection 2023. Front Psychol. 2023. PMID: 38192386 Free PMC article.
-
The Impact of Intrusive Rumination on College Students' Creativity During the COVID-19 Pandemic: The Mediating Effect of Post-traumatic Growth and the Moderating Role of Psychological Resilience.Front Psychol. 2022 Apr 11;13:789844. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2022.789844. eCollection 2022. Front Psychol. 2022. PMID: 35478749 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of caregiver burden on caregiver mental health in patients with esophageal cancer: chain mediating effects of benefit finding and rumination, a cross-sectional study.J Gastrointest Oncol. 2022 Oct;13(5):2132-2143. doi: 10.21037/jgo-22-884. J Gastrointest Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36388695 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wang H, Li Y, Chai K, Long Z, Yang Z, Du M, et al. . Mortality in patients admitted to hospital with heart failure in China: A nationwide cardiovascular association database-heart failure centre registry cohort study. Lancet Glob Health. (2024) 12:e611–22. doi:, 10.1016/S2214-109X(23)00605-8 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Hoffmann JM, Schulz A, Finke JB, Lauterbach M, Schächinger H, Vögele C, et al. . Fear of physical activity relates to cardiac interoception and symptom distress in patients with chronic heart failure. Ment Health Phys Act. (2023) 25:100553. doi:, 10.1016/j.mhpa.2023.100553 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources